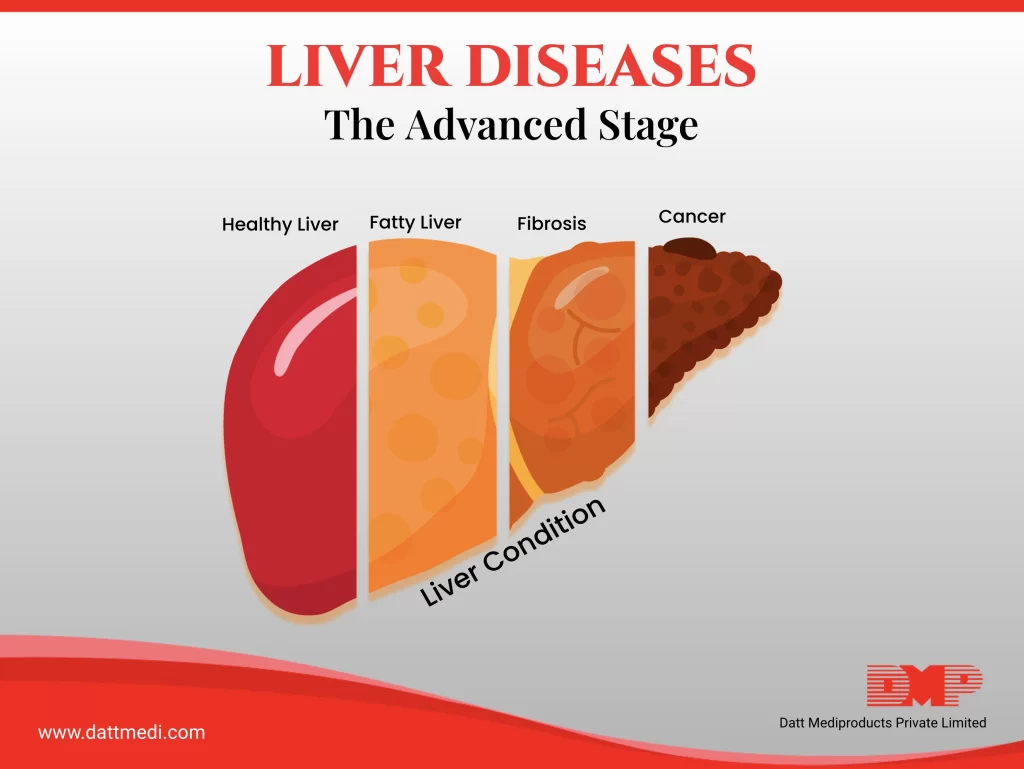
Liver diseases are on the verge of becoming the next major lifestyle diseases after Diabetes.
Do You Know?
Liver disease may affect people of any age, although a majority of patients belong to the 40-60 years age group.
In our previous blog, we discussed that liver diseases are progressive in nature and how a healthy liver becomes fatty, then develops fibrosis ultimately leading to liver cirrhosis. In this blog, we are going to discuss the advanced stages that can threaten your life.
Let’s have a look at some stats & facts:
– As per WHO Statistics, Liver Disease is the 10th most common reason for deaths in India.
– In India, Liver Disease may affect everyone in 5 individuals.
– Every year nearly 10 lakh people are diagnosed with liver cirrhosis in India.
– Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is the second most common reason for mortality due to malignancy in the world.
– Liver Cirrhosis is the 14th foremost cause of death around the world.
– Liver disease may affect individuals of any age. People may even be born with the disease.
– You may also have liver disease with no specific symptoms.
– A person with advanced-stage liver disease may bleed or bruise easily. This is because a failing liver produces fewer blood clotting proteins.
Now let’s talk about the three of the advanced stage liver diseases:
End-stage liver disease:
ESLD includes liver cirrhosis patients with irreversible decompensation signs such as hepatic encephalopathy, variceal bleed, kidney impairment, ascites, lung issues. The only treatment option left for SLD patients is a liver transplant.
Do you know that 97 percent of liver transplants in North India are Living Donor types, and the rest are cadaver transplants?
Liver Cancer:
Cancer which originates in the liver is referred to as Primary Liver Cancer. If this cancer spreads to other body parts it becomes metastatic. Liver cancer is more common in men than in women. The primary risk factor is long-term infection with the Hepatitis B or C virus because hepatitis often leads to cirrhosis which ultimately develops into cancer.
Symptoms of liver cancer may include fatigue, bloating, loss of appetite, satiety feeling, vomiting, pain especially on the right side of the upper abdomen or back and shoulder, weight loss, weakness, fever, and jaundice. Any type of liver disease may progress to liver cancer.
Liver Failure:
Failure of the liver means, liver losing all its functions. Initial symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, loss of appetite, and diarrhea. These symptoms coincide with several other common issues. As the situation progresses, symptoms become worse.
A person may become confused, disoriented, extremely sleepy with an increased risk of coma and death. Toxins back up in the brain of such patients causing a condition very similar to dementia. Liver failure is a life-threatening medical condition, with liver transplant being the only treatment option.
Do you know that a liver transplant is not a cure for liver diseases, sometimes the transplant can fail or the original disease may return.
Even a newly transplanted liver may contract liver diseases. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating low fat, low sugar, low rice- high fiber-diet, may keep liver diseases at bay.
You can visit our blog section www.dattmedi.com to know more about how to maintain a healthy lifestyle and other health topics.