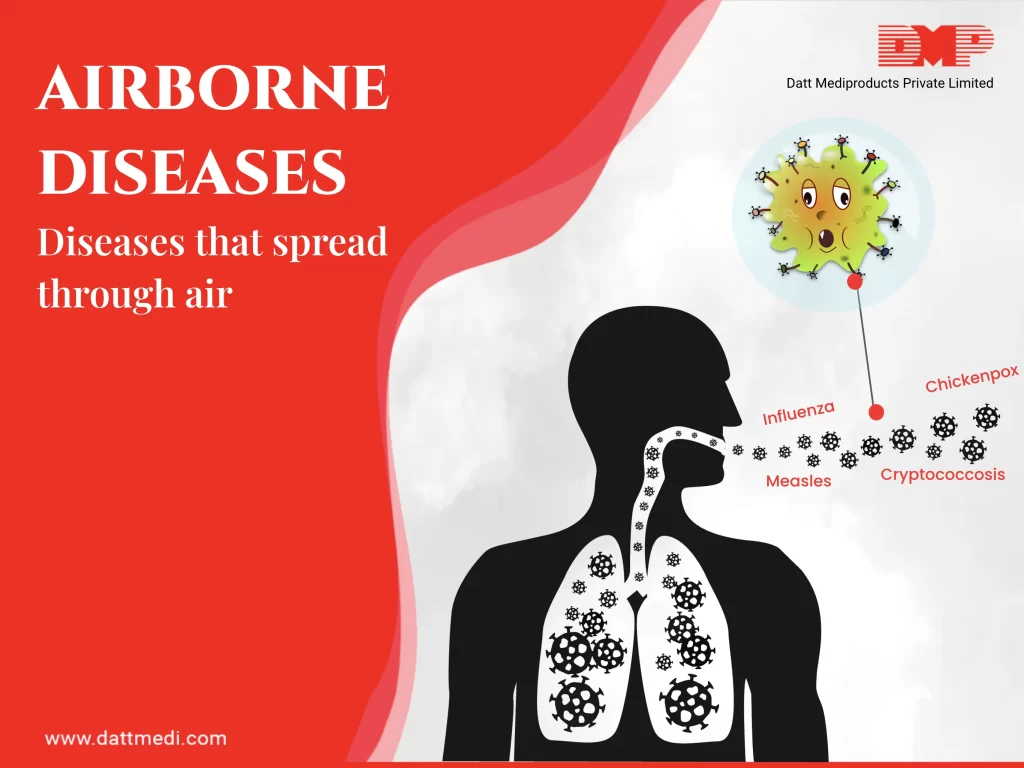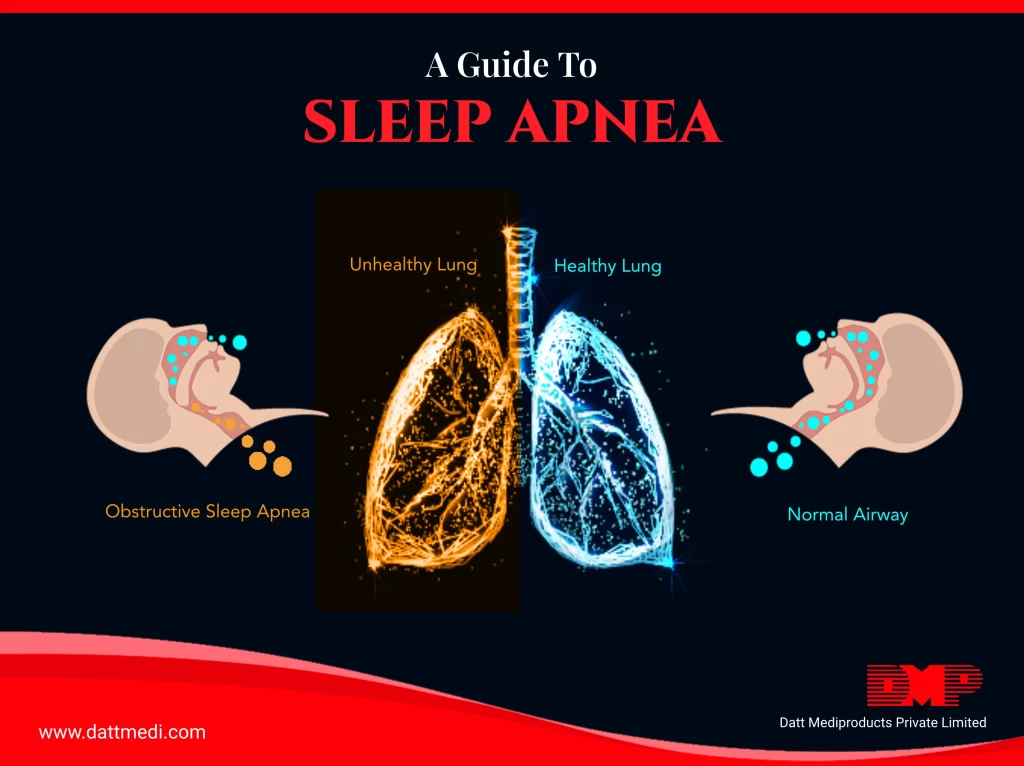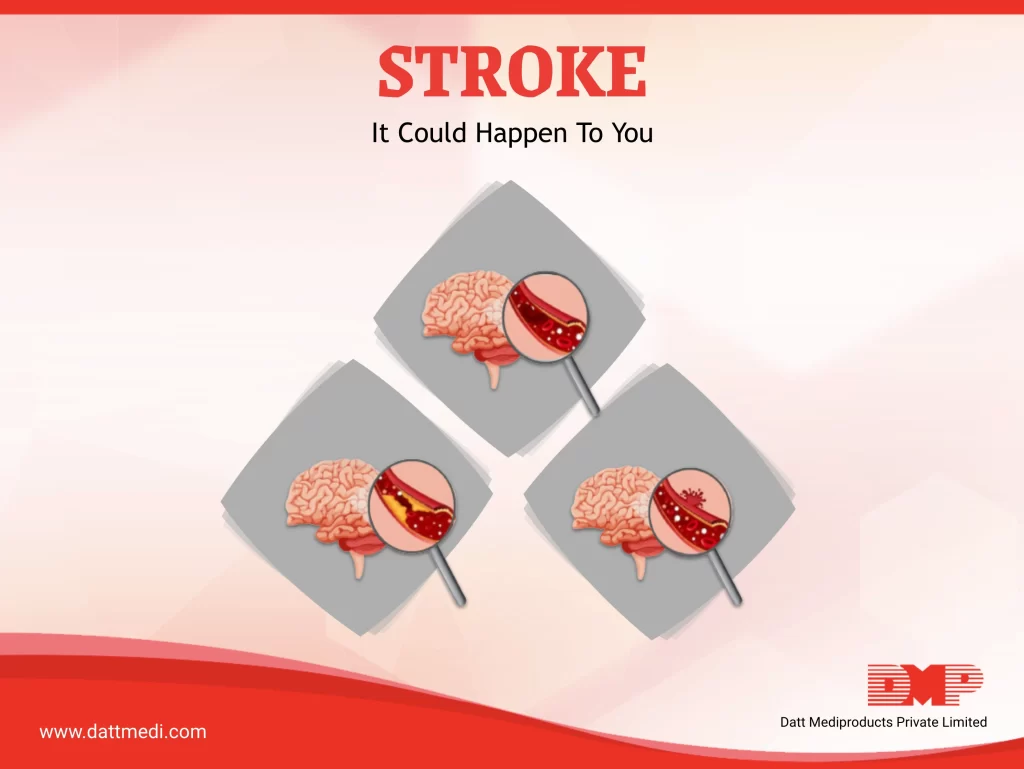
A stroke is a medical emergency causing the brain tissue to die which can lead to brain damage, long-term disability or death. A stroke is often referred to as a “brain attack” and is associated with high mortality and high morbidity.
There are a three ways in which a stroke can occur:
1. ISCHEMIC STROKE:
When the blood supply to the brain is blocked either by a clot or plaque in the artery.
2. HEMORRHAGIC STROKE:
When a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or leaks.
3. TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK (TIA), also known as a ministroke:
It is a brief interruption of blood flow to parts of the brain. A TIA may be a warning sign of a future stroke.
The 4 key symptoms to spot a Stroke are:
1. F = Face drooping or numbness
2. A = Arm weakness
3. S = Speech difficulty, slurring or inability to respond
4. T = Time to call an ambulance
Other common signs of stroke may include sudden dizziness, trouble walking, imbalance or lack of coordination, troubled vision, headache, numbness in face, arm or leg in addition to sudden confusion, troubled speech or understanding others.
In our previous blog titled “Stroke: Warning Signs” we discussed the various types of strokes in detail along with their symptoms. This blog focuses on preventive measures in addition to post stroke rehabilitation and recovery.
Preventive Measures
About 80% of strokes are preventable. The risks can be greatly reduced by taking medications or by making lifestyle changes in order to control blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
As per CDC, following are several steps which can help reduce the risk for stroke:
1. Control high blood pressure- this is one of the most important things you can do to reduce your stroke risk.
2. Eat a healthy diet low in sodium with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
3. Maintain a healthy weight.
4. Be physically active.
5. Don’t smoke, and avoid second hand smoke.
6. Limit alcohol use.
7. Prevent or manage your other health conditions, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity.
8. Get regular checkups done
STROKE REHABILITATION & RECOVERY
Stroke disability can be overwhelming to the patient and family. Post-stroke rehabilitation starts while the patient is still in hospital and can help someone who lost certain skills when part of brain was damaged during the stroke.
Several distinctive measures and trainings are available to help rehabilitate patients after stroke. These can be strength training, cognitive training, nutritional therapy, occupational therapy, mobility and balance training, motor skills exercises, psychological counselling & participation in wellbeing support groups etc. The choice of selection is based upon the presence of comorbid conditions like arthritis, kidney or other heart diseases; the severity of physical problems caused by stroke; availability of family members and insurance coverage.
The goal of these therapies & trainings is to have the stroke patient relearn simple motor activities such as walking, sitting, standing, lying down etc. and the various everyday activities such as eating, drinking, swallowing, dressing, bathing, cooking, reading, writing, and using the toilet.
In a nutshell, post stroke rehab programs aim to cover the following key components:
1. Protect the patient from developing new medical issues such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, or a clot formation in large veins.
2. Restore lost strength & balance
3. Rebuild speech & cognitive functions
4. Prevent recurrences & complications
5. Improve overall quality of life
We @dattmediproducts understand that rehabilitation programs play a predominant role in helping patients regain their lost/ affected skills, and be independent again. Though recovery may be a lengthy process but dedication and strong will power for improvement can help to gain the most benefit.
Visit us at www.dattmedi.com to read more.