Parkinson’s disease is a complex and often misunderstood neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by a progressive loss of dopamine-producing cells in the brain, leading to a range of motor and non-motor symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. In this blog, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Parkinson’s disease, as well as the importance of support and advocacy for those living with the condition.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease:
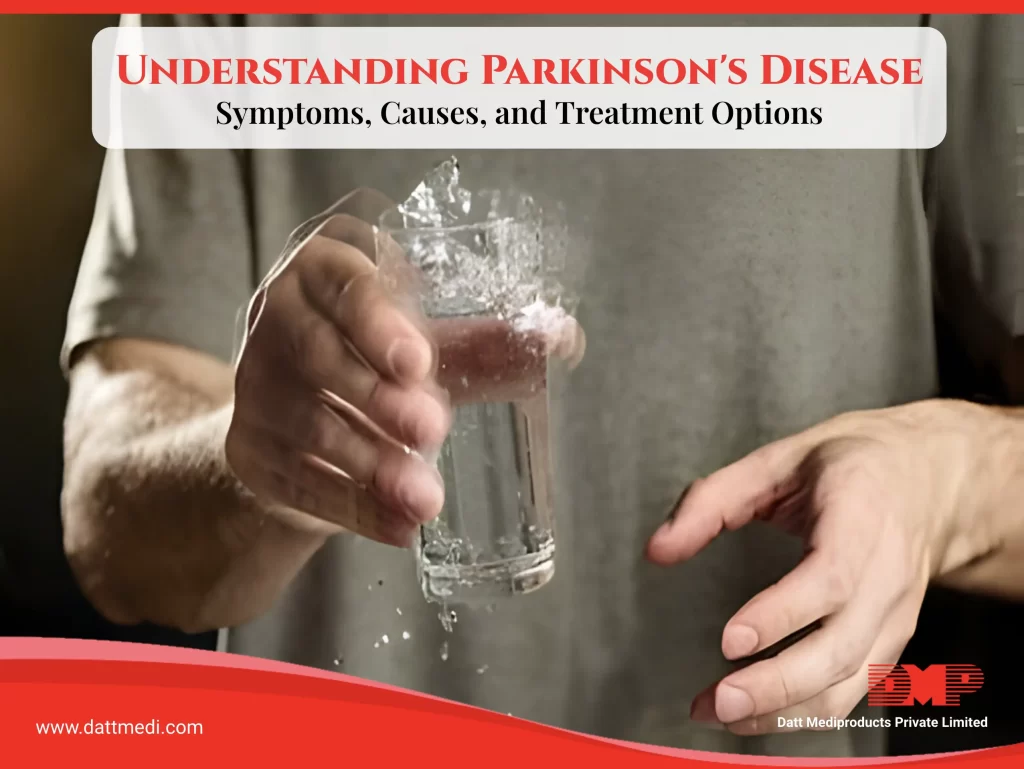
Parkinson’s disease primarily affects movement, causing a variety of motor symptoms that can vary in severity from person to person. The most common symptoms include tremors, stiffness, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement). Individuals with Parkinson’s may also experience freezing gait, a sudden inability to initiate or continue walking, as well as a stooped posture and changes in speech and handwriting.
In addition to motor symptoms, Parkinson’s disease can also cause a range of non-motor symptoms that may be less visible but equally challenging. These can include depression, anxiety, cognitive impairment, sleep disturbances, and autonomic dysfunction. It is important for individuals with Parkinson’s and their caregivers to be aware of these non-motor symptoms and seek appropriate support and management strategies.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is not yet fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Advancing age is the most significant risk factor, with the majority of cases diagnosed in people over the age of 60. However, younger individuals can also develop Parkinson’s, particularly if they have a family history of the disease or are exposed to certain environmental toxins such as pesticides and solvents.
Recent research has also identified specific genetic mutations associated with an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease, although these account for only a small percentage of cases. Overall, Parkinson’s is thought to result from a complex interplay of genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers, and further research is needed to fully understand these mechanisms.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies:
While there is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease, there are a variety of treatments available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Medications such as levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors can help alleviate motor symptoms by increasing dopamine levels in the brain. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can also be beneficial in addressing specific motor and non-motor symptoms.
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, healthy diet, and stress management techniques can also play a key role in managing Parkinson’s disease. Social support and community resources are also invaluable for individuals living with Parkinson’s and their caregivers, providing emotional support, practical assistance, and opportunities for socialization.
Support and Advocacy:
In India, there are several organizations dedicated to supporting individuals with Parkinson’s disease and raising awareness about the condition. One such organization is the Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorder Society (PDMDS), which offers rehabilitation programs, support groups, and educational resources for people living with Parkinson’s and their families. The Indian Parkinson’s Disease Association (IPDA) is another valuable resource, providing information, advocacy, and support services to improve the lives of those affected by Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease is a challenging and complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management and care. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Parkinson’s, as well as the importance of support and advocacy, we can work together to improve the lives of individuals living with this condition. Through education, awareness, and community involvement, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by Parkinson’s disease.