Cerebral Palsy is a neurological developmental disorder that affects body’s movement. “Cerebral” means brain and “Palsy” means the impairment or loss of motor function. Cerebral Palsy results from an interference in brain development affecting the person’s ability to control his or her muscles.
It may also be caused due to an impaired blood supply, decreased oxygen, glucose or calcium supply, infections, trauma & preterm birth. It is the most common childhood impairment which may occur during early months of pregnancy, during birth, soon after birth or early childhood.
SYMPTOMS
The signs and symptoms of this disorder vary greatly from person to person as the condition may affect the entire body or a part of it. In general, a person suffering from this disorder will have problems with movement and coordination, speech and eating, development, and various others.
1. The Movement and Coordination Symptoms may include Stiff or tight muscles and exaggerated reflexes (spasticity), Stiff muscles with normal reflexes (rigidity), Lack of balance and muscle coordination (ataxia), Tremors or jerky involuntary movements, Slow, writhing movements, Difficulty walking etc.
2. The Speech and Eating Symptoms may include delays in speech development, Difficulty speaking, Difficulty with sucking, chewing or eating in addition to Excessive drooling or problems with swallowing
3. The Development Symptoms may include Delays in reaching motor skills milestones, such as sitting up or crawling, Learning & Intellectual difficulties, delayed growth, resulting in smaller size than would be expected
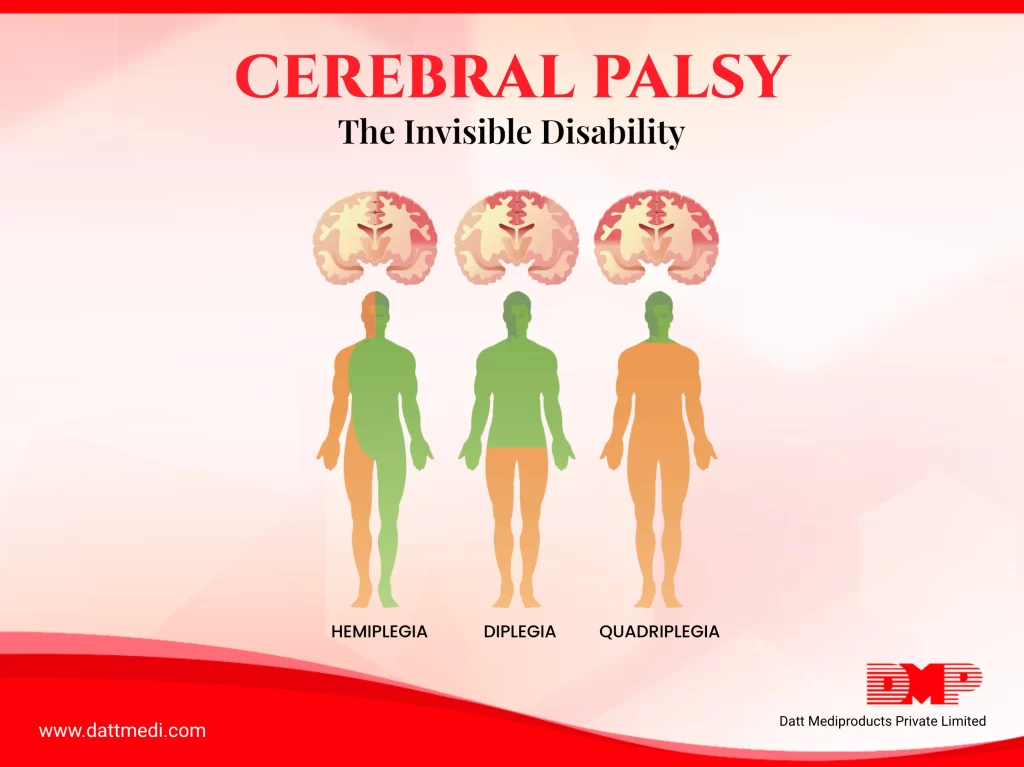
TYPES
Cerebral Palsy may be classified as per the main type of movement disorder involved which may be based on the area of the brain which gets affected. The movement disorders can be Stiff muscles (spasticity), Uncontrollable movements (dyskinesia) and Poor balance and coordination (ataxia)
1. Spastic Cerebral Palsy: This is the most common type affecting 80% of CP patients. Muscles may be stiff causing awkward movements and can affect any body part such as legs (Spastic diplegia/diparesis); one side of the body (Spastic hemiplegia/hemiparesis); all four limbs, the trunk, and the face (Spastic quadriplegia/quadriparesis).
2. Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy: This is characterized by uncontrollable movements of hands, arms, feet, and legs, making it difficult for the patient to sit and walk. It makes it difficult to swallow, suck or talk when face and tongue are affected.
3. Ataxic Cerebral Palsy: This type causes problems with balance and coordination.
4. Mixed Cerebral Palsy: Having more than one type of CP, for example spastic-dyskinetic CP
CAUSES & RISK FACTORS
There are a certain factors or medical conditions that can happen during any pregnancy or delivery which increase the risk that a baby is born with cerebral palsy. These could be low birthweight (usually less than 5 ½ pounds); premature birth (before 37 weeks); Twins, triplets, and other multiple pregnancies with the death of a baby’s twin or triplet further increasing the risk; Infections such as toxoplasmosis, rubella (German measles), cytomegalovirus, and herpes infecting the womb or placenta may go on to damage the developing nervous system in an unborn baby; Mothers with thyroid abnormalities, intellectual disability, excess protein in the urine, jaundice or seizures are slightly more likely to have a child with cerebral palsy.
PREVENTION
Although, the condition may not be prevented but the risks may be restrained in the following ways:
1. Those who are planning pregnancy can get vaccinated beforehand especially against diseases such as rubella. Doing this may ward off an infection that could cause foetal brain damage.
2. Regular visits to doctor may reduce health risks for both mother and the unborn baby.
3. Avoiding alcohol, tobacco and illegal drugs are a good way to prevent cerebral palsy as they have been linked to it.
TREATMENT
The condition differs from person to person in terms of type and severity. It’s important for healthcare providers to develop a customized/ individualized plan of treatment. Physical therapies, occupational therapies and Speech & language pathology can be used to address different issues.
Cerebral palsy is a lifelong disorder. There is no cure yet but an individualized plan of treatment can help improve function. Follow us at www.dattmedi.com for more health related blogs.
Stay updated, Stay Healthy!




