
Anxiety and Depression are two of the most common psychiatric illnesses, which have become a major public health concern worldwide. Both conditions are treatable and highly comorbid.
“Approximately around 50% of people diagnosed with depression can also be diagnosed with an anxiety disorder”– Anxiety & Depression Association of America.
Anxiety may occur as one of the symptoms of clinical depression and can also act as a trigger for it. A number people get diagnosed with both anxiety disorder and clinical depression with women twice likely to be affected by Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Depression as men.
What is Depression & Anxiety?
Depression is a common and one of the most serious medical illnesses that negatively affects how a person feels, the way he/she thinks and how he/she acts. It causes feelings of sadness with or without a loss of interest in activities once relished. There are a lot of emotional and physical problems associated with Depression or Major Depressive Disorder which can negatively affect a person’s ability to function at work and at home. As per WHO, an estimated 3.8% of the world’s population are affected by Depression, including 5.0% among adults and 5.7% among adults older than 60 years.
Anxiety, on the other hand, is a feeling of worry, fear, nervousness, or unease, usually related to an imminent event or something with an undetermined outcome. These feelings become a disorder when their amount and frequency interferes with person’s daily life activities.
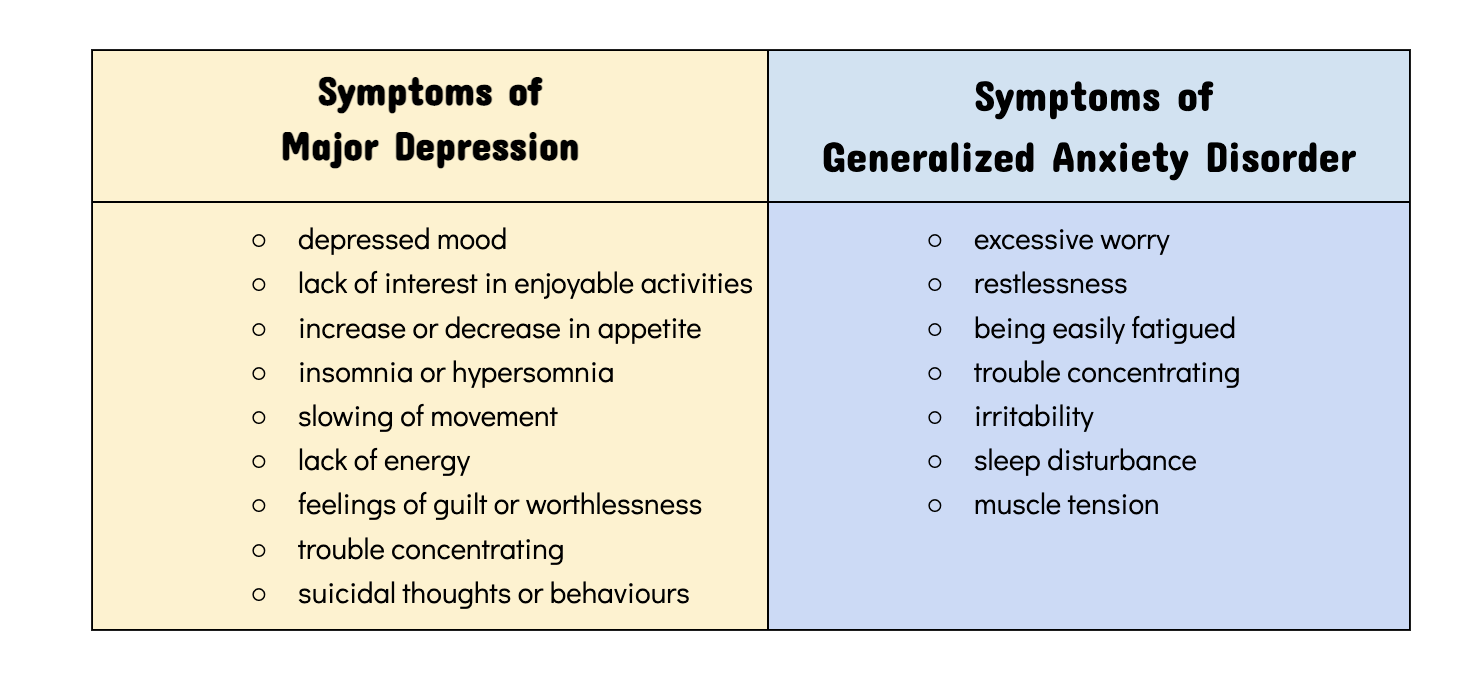
CHARACTERISTICS OF ANXIETY & DEPRESSION
Both the conditions are different but there are certain depression symptoms which are similar to anxiety disorders. These could be nervousness, irritability, fatigue and problems while sleeping and concentrating.
Although, anxiety and depression are comorbid conditions, there are some distinguishing features too.
Anxiety disorders and depression both occur during development stage, with the former commonly beginning during preadolescence and early adolescence age and the latter tending to emerge during adolescence and early to mid-adulthood.
People with depression move slowly, with flat and dull reactions. People with anxiety tend to be more keyed up, while struggling to manage their racing thoughts.
People with anxiety have a presence of fear about future. Depressed people who do not have overlapping anxiety are less likely to be worried about future events, as they are in continual belief that things will continue to be bad. In other words, they may predict the future based on their current feelings.Treatment & Management Techniques
Symptoms of both these conditions usually improve with the help of specialist psychological counselling (psychotherapy), medications, such as antidepressants, or both of these. Lifestyle changes, such as improving sleep habits, eating habits, enhancing social/family support, indulging in stress-management techniques or getting regular exercise, also help in controlling these conditions. Avoiding alcohol, smoking and recreational drugs may also help, as they make either of these conditions worse and interfere with treatment.
It is normal to have blues at times or feeling down now and then. But if these ongoing feelings become severe, then it could be an underlying mental health disorder.
You may read our previous blogs on Depression and Anxiety to know more about these two mental illnesses and Tips to Keep Positive. Follow us @dattmediproducts to stay updated.




