Our body needs insulin to transform glucose into energy. Diabetes occurs when the pancreas in our body is not able to make insulin, or when our body is unable to use the insulin produced.
Lack of insulin or the inability to use insulin leads to raised glucose levels in our blood. This condition is called “hyperglycaemia”.
Do you Know?
Diabetes is a chronic condition and can’t be cured. But it can be effectively managed or successfully treated to stay healthy.
TYPE 1 DIABETES:
The body fails to produce insulin. It is an autoimmune disease, in which the antibodies that are produced attack & destroy the pancreatic cells, which produce insulin.
TYPE 2 DIABETES:
The body doesn’t make insulin or is not able to use the insulin produced because the body becomes insensitive/ resistant to it.
What is Insulin & How it works?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas, which helps to convert glucose, from the food we eat, into energy. All carbohydrate foods are broken down into glucose in the bloodstream. Insulin circulates in the blood and acts as a key to let this glucose get into the cells and help the body produce energy.
Insulin helps to regulate the blood sugar levels in our bloodstream by lowering the amount of glucose/sugar in the bloodstream when it is too high (hyperglycemia). When the blood sugar levels drop then the secretion of insulin from the pancreas also reduces thereby stopping the level from falling to low (hypoglycemia).
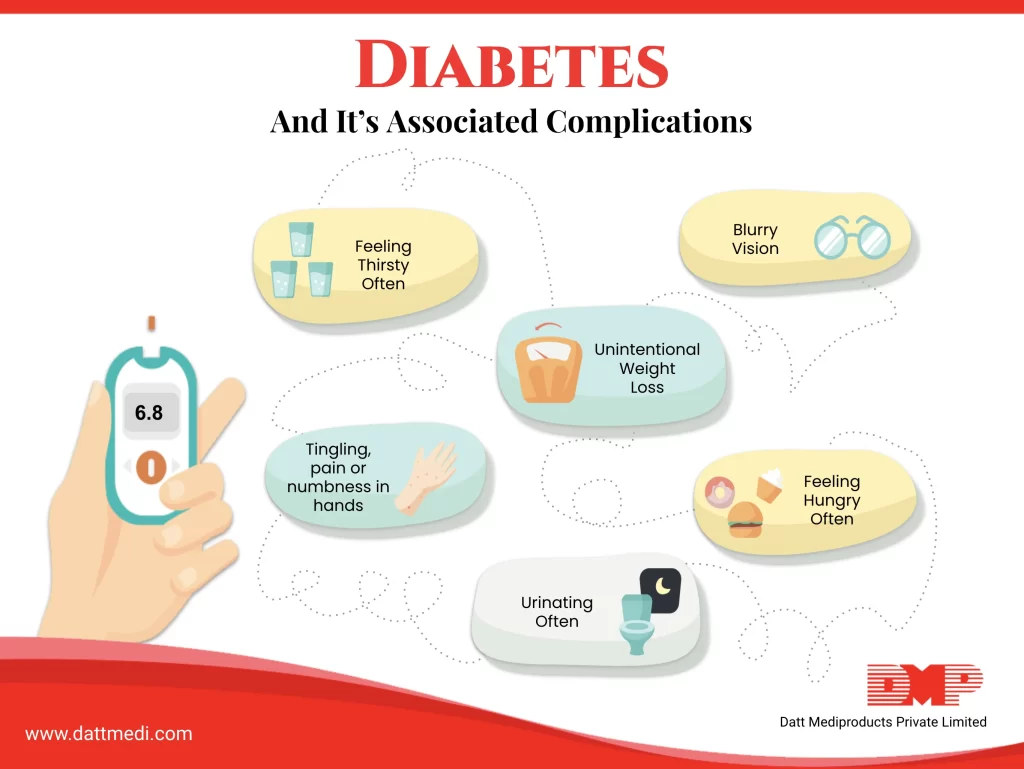
How do you feel if you are Diabetic?
Diabetic patients may show the following symptoms:
- Frequent Urination
- Excessive Thirst
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Excessive Hunger
- Fatigue
- Skin Problems
- Blurred Vision
- Slow Healing Sores/Wounds
- Yeast Infections
- Tingling Sensation or Numbness in the Feet or Toes
Type 1 & Type 2 diabetes, can develop at any age though Type 1 appears more commonly during childhood or adolescence and Type 2 is more common in people older than 40. If not managed for the long term, high blood glucose levels can increase the risk of some serious complications and failure of various organs and tissues. Let us discuss the various complications of diabetes, which develop gradually.
Complications associated with Diabetes
The complications associated with diabetes are long term and develop gradually. If you don’t control your blood sugar and are suffering from diabetes for a long time, the risk of developing the complications increases.
Some of the possible complications may include the following:
NEUROPATHY:
Neuropathy occurs when a nerve gets damaged & malfunctions. Excess blood sugar damages the blood capillaries, which nourish the nerves, especially in lower limbs, causing neuropathy with symptoms like numbness, tingling/pin pricking sensations, burning or pain. If left untreated, limbs may lose their sensation.
NEPHROPATHY: Nephropathy occurs when our kidneys get damaged. In Diabetes, the delicate filtering system, consisting of millions of tiny blood vessel clusters (glomeruli), gets damaged which usually filters out the waste from the blood.
RETINOPATHY: Diabetes damages the blood vessels supplying blood to the retina causing “Diabetic Retinopathy”. Diabetes increases the risk of some serious vision complications like glaucoma, cataracts and even has the potential to cause blindness.
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES: The chances of CVDs, like coronary artery disease, angina, heart attack, stroke, and atherosclerosis, increase with diabetes.
Other diabetes-associated complications may include Foot damage, skin problems like bacterial & fungal infections, hearing impairment, depression and Alzheimer’s.
We @DattMediproducts understand the harmful effects of diabetes and we also understand that if not managed, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening.
Healthy lifestyle changes remain essential.
We recommend getting your blood sugar levels checked on a regular basis to avoid serious complications that can be avoided if your sugar is kept regulated and consult a physician at the earliest if diagnosed.




