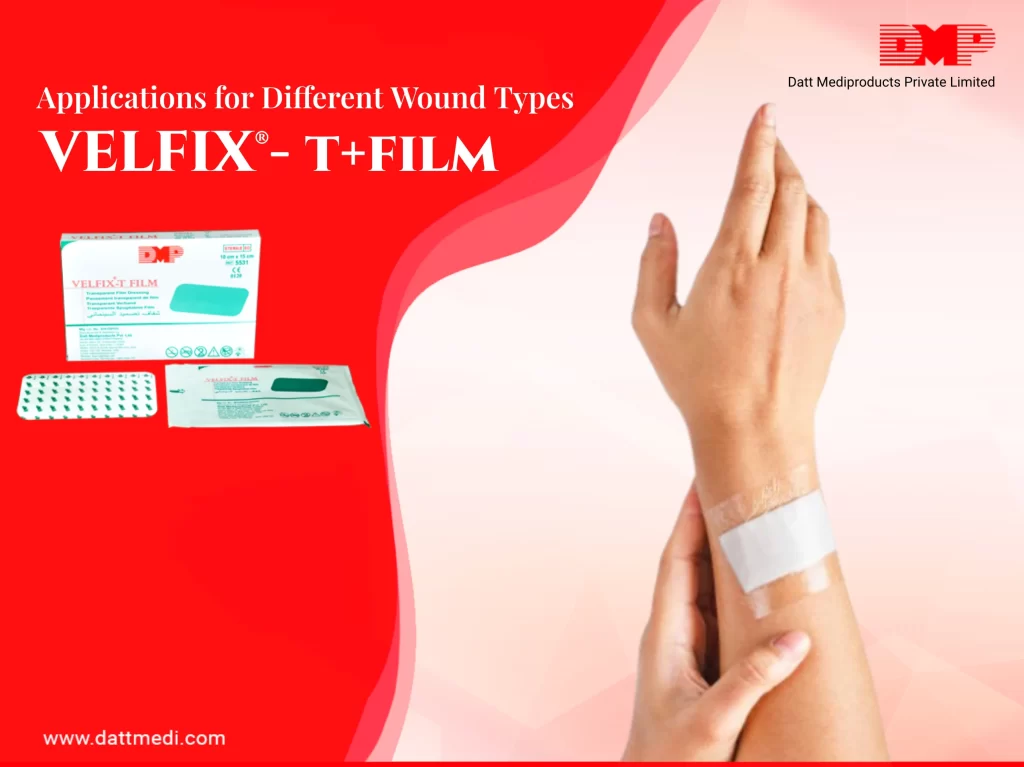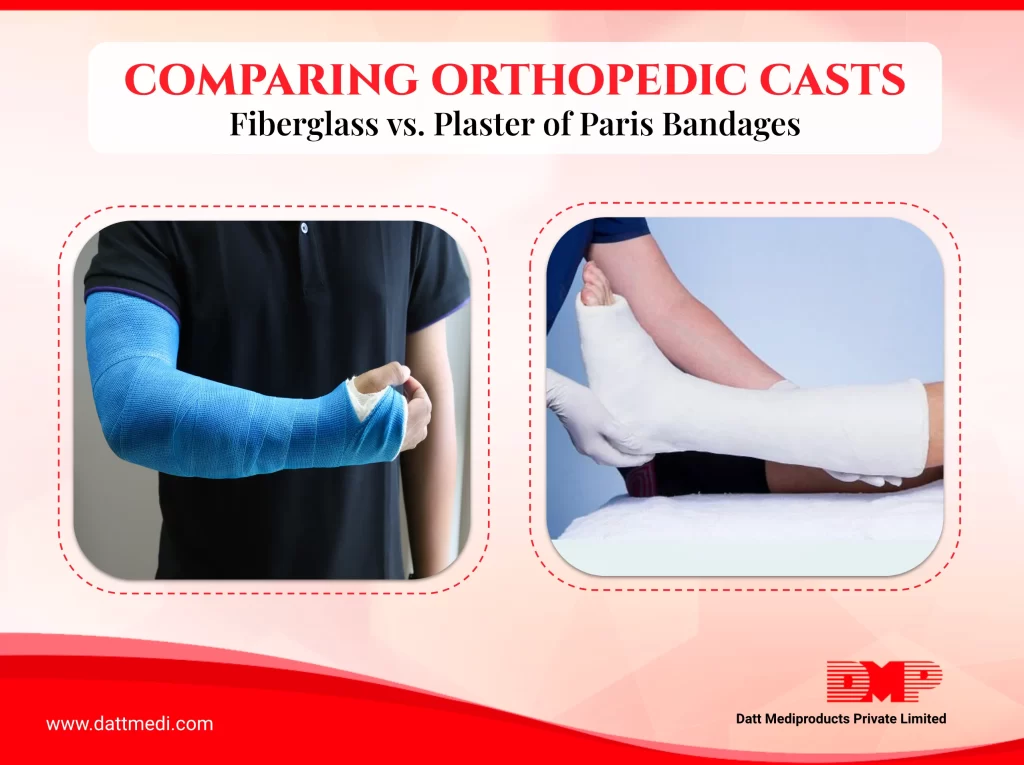
When it comes to managing fractures, the choice of cast material can make a significant difference in a patient’s recovery experience. Orthopaedic casts are essential in ensuring that broken bones heal correctly by providing the necessary immobilization. Two popular options in the medical field are Fiberglass and Plaster of Paris (POP) bandages. But how do they compare? Let’s dive into the details.
A. Material Composition: The Building Blocks
The fundamental difference between these two types of bandages begins with what they are made of:
Fiberglass is a synthetic material, made from plastic fibers coated with a resin. It’s known for being lightweight and is often available in various colors, which can add a bit of personality to an otherwise clinical experience.
Plaster of Paris is made from a fine white powder called gypsum. When mixed with water, it forms a thick paste that hardens as it dries.
B. Application Process: Ease vs. Skill
Applying these bandages requires different techniques:
1. Fiberglass bandages are dipped in water, applied to the injury, and begin hardening almost immediately, which allows for quick and efficient application. This makes it easier for healthcare providers to mold it perfectly to the patient’s body.
2. Plaster of Paris bandages need to be soaked in water and take longer to set. While they require more skill to apply, they offer a smooth finish that many patients find comfortable.
C. Durability and Strength: Which Lasts Longer?
When considering durability:
1. Fiberglass is the champion of strength. Its resistance to wear and tear makes it ideal for active individuals or cases requiring long-term immobilization.
2. Plaster of Paris is less durable, with a tendency to chip over time, making it better suited for short-term casts or initial treatments.
D. Comfort and Breathability: Feeling at Ease
Comfort is a top priority for patients who need to wear a cast for an extended period:
1. Fiberglass is lighter and less bulky, which adds to the patient’s comfort. However, it can sometimes be less breathable, leading to potential discomfort in hot or humid climates.
2. Plaster of Paris is bulkier and heavier, but it’s smooth finish can be more comfortable for some, allowing the skin to breathe better.
E. Setting Time and Ease of Use: Quick vs. Steady
The time it takes for a cast to set is crucial:
1. Fiberglass sets in just a few minutes, enabling patients to resume limited activities sooner.
2. Plaster of Paris takes much longer, often up to 15 minutes, which can be a disadvantage when immediate mobility is needed.
F. Water Resistance and Hygiene: Keeping It Clean
Hygiene is another critical factor:
1. Fiberglass is water-resistant, making it easier to maintain and less likely to harbour bacteria.
2. Plaster of Paris does not resist water and can easily disintegrate if exposed to moisture, requiring patients to take extra precautions to keep it dry.
G. Cost and Accessibility: Budget Matters
Cost and availability can influence the choice:
1. Fiberglass is typically more expensive and may not be available in all healthcare settings.
2. Plaster of Paris is more affordable and widely accessible, making it the go-to option in many clinics and hospitals, especially in resource-limited settings.
H. Environmental Impact: Think Green
With growing awareness about environmental impact:
1. Fiberglass, being a synthetic material, is less eco-friendly and can pose disposal challenges.
2. Plaster of Paris is derived from natural materials and is more environmentally friendly, though proper disposal is still necessary.
I. Clinical Applications: The Right Cast for the Right Case
1. Fiberglass is often recommended for long-term use and in cases where the patient is likely to remain active.
2. Plaster of Paris is ideal for short-term immobilization or initial treatments, particularly when budget constraints are a concern.
Making the Right ChoiceChoosing between Fiberglass and Plaster of Paris bandages depends on several factors, including the patient’s lifestyle, the duration of immobilization, and budget.
Fiberglass is generally favoured for its durability and water resistance, while Plaster of Paris remains a trusted option for initial and short-term care due to its affordability and ease of use.
For more insights and to explore our range of orthopaedic casting products, visit our website: Velcast™ – Orthopaedic Fiberglass Casting Tape, Osteopop™ – Plaster of Paris Bandage and Velpop® – Plaster of Paris Bandage. Discover the best solutions for your orthopaedic needs today!