
Haemophilia is a bleeding disorder in which the blood doesn’t clot normally because of the absence of some vital clotting factors. It is an X-linked congenital bleeding disorder.
Following are the two common types of Haemophilia:
1. Haemophilia A (Classic Haemophilia): Haemophilia A is caused by a lack or decrease in the levels of clotting factor VIII.
2. Haemophilia B (Christmas Disease): Haemophilia B is caused by a lack or decrease in the levels of clotting factor IX
Hemophilic patients bleed for a longer time than normal patients. The smaller external cuts do not cause to much worry but the deep bleeding internal wounds area a matter of grave concern normally. This internal bleeding may result in tissues or organ damage and may be life threatening also. The severity of the condition depends upon the amount of the factors in the blood.
The only treatment modality available includes regular replacement of the missing clotting factors. But this is a costly affair and the factor concentrates are not affordable by all. Some people may encounter adverse reactions when their system develops inhibitor proteins inactivating these clotting factors and make the treatment less effective.
We introduce a cost-effective alternative to the factor replacement therapy in the management of external bleeds in Haemophilic patients. We present “VELSEAL-T”: a novel hemostatic device which can be used as an aid to prevent profuse bleeding in hemophilia patients with external injuries.
VELSEAL-T: An Innovative Haemostatic Device
VELSEAL-T is an innovative hemostatic medical device to control bleeding. The device is incorporated with a clotting agent and anti-fibrinolytic agent. The clot promoting and clot stabilizing agents enable rapid blood coagulation when the blood flows into the dressing, leading to sealing and stabilization of the wound surfaces.
The VELSEAL-T is developed and manufactured by Datt Mediproducts and has been used to control bleeding in patients without bleeding disorders. However, when it was used in hemophilic patients, the hemostatic action was evident. This is because the coagulation process of blood entering the matrix of VELSEAL-T is enhanced by the presence of clotting factors.
– Haemophilia A patients lack clotting Factor IX because of which Prothrombin doesn’t get converted into Thrombin. Thereby, a stable clot is not formed and patients bleed for a longer than the normal patients.
– VelSeal-T contains Thrombin which catalyzes the conversion of inactive fibrinogen into active fibrin that forms the clot.
– Tranexamic acid present in VelSeal-T is an anti-fibrinolytic agent which helps in clotting and also stabilizes the clot.
The use of VELSEAL-T in Haemophilia patients may significantly reduce morbidity and may provide cost-effective treatment for minor trauma in a setting where factor concentrate is prohibitively costly and not widely available.
CASE STUDY REPORT
This case study was published in the Journal of Haemophilia Practice in the year 2018. The study was conducted at Assam Medical College and Hospital (India).
Patients Details: Age: 36 years Occupation: Shopkeeper Background: Relatively poor socioeconomic status Medical History: Suffering from mild hemophilia A (serum factor VIII level 8%). Factor IX levels were found to be within normal limits. He was not on prophylactic treatment due to economic constraints
Problem: He was presented with profuse bleeding from the forehead after an injury following a fall on the concrete surface. Initially, pressure and ice were applied to the area of injury, to the left temporal area of his forehead. This didn’t help much and the bleeding continued when the pressure was released. The patient also developed a periorbital hematoma (black eye) rapidly. He attended hospital 18 hours after injuring himself.
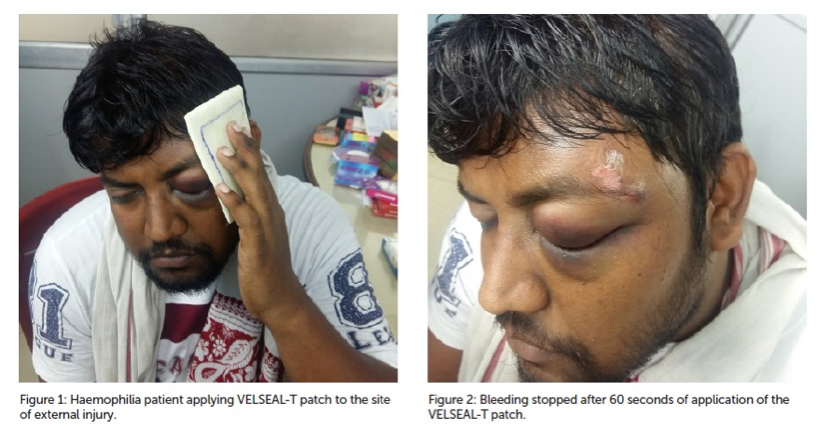
In case of unavailability of Desmopressin (DDAVP), VELSEAL-T was procured from the Department of Medicine. The product was discussed with the patient and the proper consent was obtained before using it.
The VELSEAL-T patch was applied to the site of external injury, on the left temporal area of his forehead. The patient was told to hold the patch in place for two minutes but the bleeding was stopped after 60 seconds.
The patient was asked to hold the dressing in place for another 60 seconds. After two minutes of applying pressure using the VELSEAL-T patch, there was no further oozing of blood from the injury site.
Do You Know: Desmopressin (DDAVP®) is used to help blood clotting in patients with von Willebrand’s disease or mild hemophilia A as it induces an increase in plasma levels of von Willebrand factor (VWF), coagulation factor VIII (FVIII), and tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA).
This case study published in the Journal of Haemophilia Practice shows that VELSEAL-T is a safe and cost-effective treatment method to stop external bleeding in Haemophilia patients. Its use may significantly reduce the requirement for costly factor concentrates, especially in developing countries like India with significant resource constraints and where patients do not have access to factor concentrate and hence bleed profusely even with minor trauma.
Note: Proper consent was obtained from the patient to publish his case history and photograph the bleeding site, including his face. This was also recorded in his native language (Assamese).




