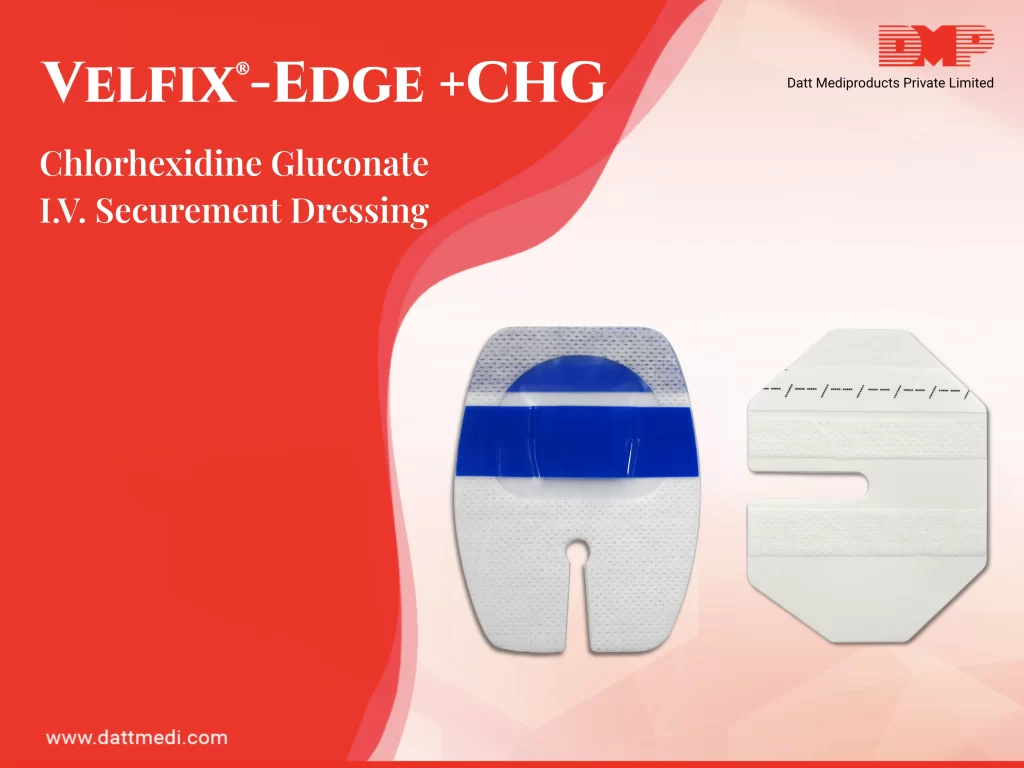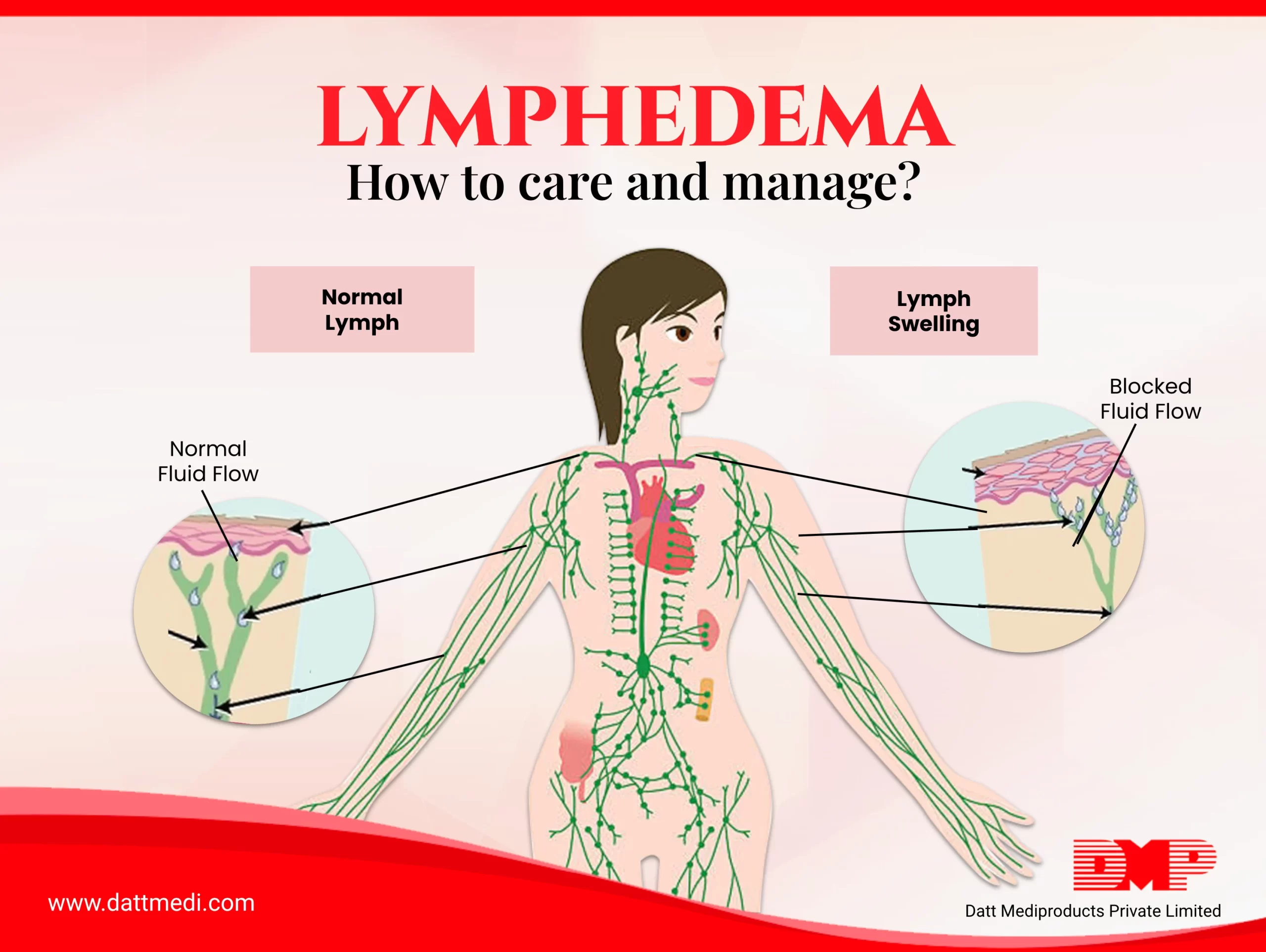
Lymphedema is a chronic disease associated with the lymphatic system, which results in swelling in one or more parts of the body. It usually develops in the arms or legs due to the accumulation of lymph fluid.
This condition occurs when the lymph fluid doesn’t flow properly in the lymphatic vessels due to the loss of lymph nodes or a blockage resulting from cancer treatment, trauma, surgeries etc.
A person suffering from Lymphedema in arm or leg may show the following symptoms:
- Swelling or puffiness
- A feeling of tightness or heaviness
- Decreased flexibility
- Pain or discomfort
- Recurring infections
- Hardening and thickening of the skin (fibrosis)
Lymphedema can be classified in the following types:
Primary Lymphedema – is caused by a rare genetic development disorder affecting the lymphs. The symptoms usually develop during infancy or puberty.
Secondary Lymphedema – is caused by damage to the lymphatic system from any injury, infection, surgery, cancer treatment, etc. Secondary lymphedema is more common than the primary type, it affects around 2 in 10 women with breast cancer.
How does lymphedema develop in cancer patients?
The surgery involved in the treatment of breast cancer patients often leads to the removal of lymph nodes. The removal of a minimum of two or three lymph nodes from under the arm is called a sentinel lymph node biopsy and when a greater number of nodes are removed, it is referred to as axillary lymph node dissection.
Radiation therapy also causes damage to the lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels. Over a period of time, the lymph fluid gets accumulated as it doesn’t flow properly because of lymphatic system damage and this causes the swelling.
How can we manage lymphedema?
Lymphedema can’t be cured. There are a few treatment methods available, like compression treatments and physical therapy, which may help to reduce the swelling, discomfort and other symptoms.
Following are few of the available “MEDICAL MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES”:
- Compression Bandages: Compression Bandages encourage the lymph to flow more evenly and reduce the fluid re-accumulation. This works by stimulating the lymph flow through the damaged lymph nodes or lymphatic vessels and reducing swelling by preventing the fluid to collect in the affected area.
- Stockings: Stockings or elastic sleeves must fit properly around the limb to ensure gradual compression from the distal end towards the proximal end.
- Pneumatic Compression devices: These are the stockings or the sleeves which are connected to a pump for providing compression. These help to prevent long-term scarring. However, these can’t be used in patients with congestive heart failure, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) etc.
- Complex Decongestive Therapy: This includes massage techniques involving slow, repetitive stroking & light circular movements, to evenly distribute the lymph fluid from the distal end towards the body. This is also known as manual lymphatic drainage.
- Exercise: Exercise may be prescribed by the doctor or the therapist. These exercises may include those which help to stimulate the lymph flow.
Risks & Complications:
The major function of lymph nodes is to filter out the bacteria and other toxins so that they don’t enter our blood. The removal of lymph nodes after the surgery or radiation therapy could lead to further complications like infections, whether or not the patient develops lymphedema.
Even small cuts and breaks in the skin can get infected. This can then lead to serious bacterial infection like CELLULITIS which could spread rapidly and could be life threatening also. Cellulitis would need immediate medical attention and treatment with antibiotics. Skin and tissue infections associated with lymphedema must be treated with antibiotics to avoid any kind of Sepsis.
Prevention is always Better
Cancer patients who have undergone surgery or radiation therapy may ask their doctor if the therapy will affect lymph nodes or lymph vessels. Below are some of the methods which can help reduce the risk of the lymphedema getting worse. Protect the lymphedematous arm or leg from any injury which may invite infections.
- Provide rest to the affected limb while recovering after cancer treatment.
- Avoid overexertion, heavy lifting and only perform the exercises prescribed by the doctors.
- Protect the lymphedema affected limb from extreme cold and heat.
- Elevate the limb above the level of your heart, whenever it’s possible.
- Any tight clothing which could constrict the limb should be avoided.
- Keep the lymphedematous limb clean. The outer layer of the skin is the body’s natural protection barrier, any breaks in the skin could invite infections.
- Never allow injections or blood draws from the affected limb.
Advantages of Compression Bandages in Managing Lymphedema
Compression bandages are an effective management technique to reduce the build-up of the lymph fluid volume in a lymphedematous limb in the following ways:
- Reduces capillary filtration
- Shifts the fluid into the non-compressed parts of the body
- Increases the lymphatic reabsorption and stimulate lymphatic transport
- Improves the venous pump in patients with veno-lymphatic dysfunction
- Breaks fibrosclerotic tissue
We @ Datt Mediproducts manufacture and market multi-layered compression bandages of impeccable quality following international standards.