Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are one of the most prevailing adverse events among hospitalized patients. These nosocomial infections are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among critically ill hospitalized patients, especially in intensive care units (ICUs).
The most serious among these infections develop at the vascular access sites and are called as the Central Venous Catheter-associated Bloodstream Infections (CVC-BSIs) or may also be labeled as the Catheter-Related Blood Stream Infections (CRBSI).
Such bloodstream infections are associated with an increased healthcare cost and duration of hospital stay and in some cases, morbidity. However, it is possible to prevent and treat these serious infections.
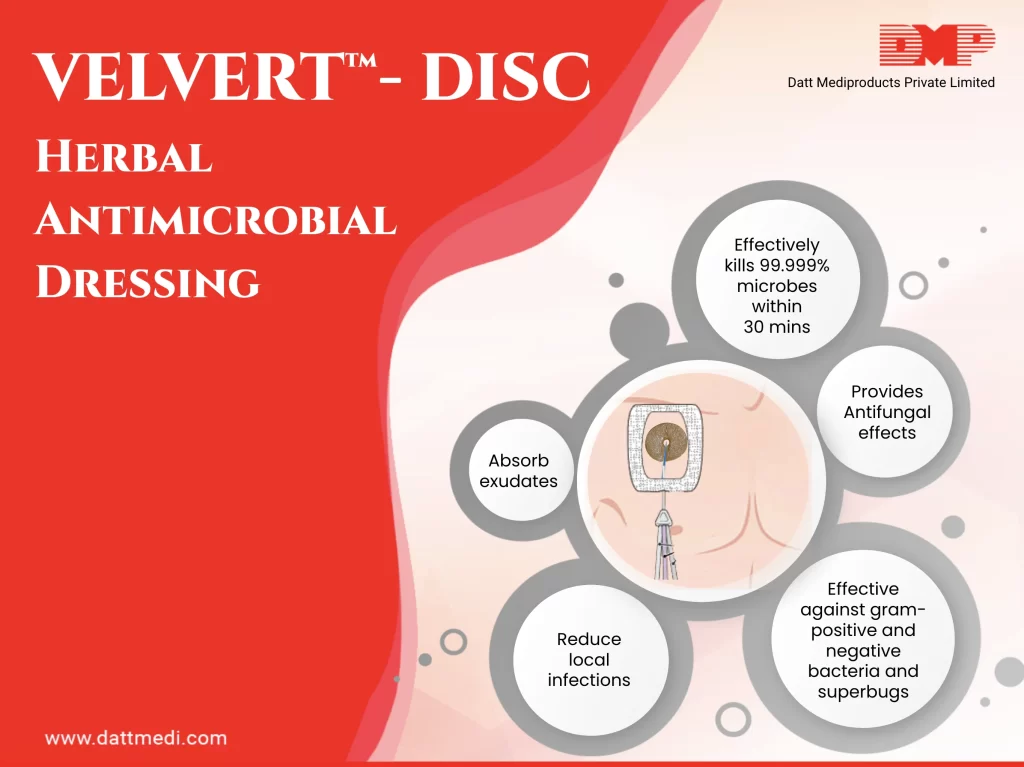
We, Datt Mediproducts introduce an ingenious product “VELVERT-DISC”. The product is intended to reduce local infections, catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSI), and skin colonization of microorganisms commonly related to CRBSI, in patients with central venous or arterial catheters.
What is VELVERT-DISC?
Velvert Disc is a herbal based antimicrobial barrier dressing which can be used to absorb exudates and to cover a wound caused by the use of vascular and non-vascular percutaneous medical devices such as IV catheters, central venous lines, arterial catheters, dialysis catheters, peripherally inserted coronary catheters, midline catheters, drains, chest tubes, externally placed orthopedic pins, and epidural catheters. Velvert Disc provides immediate and continuous antimicrobial protection with the integrated herbal antimicrobial formulation.
COMPOSITION:
Velvert Disc is a unique and novel product. It comprises some patented herbal antimicrobial formulations. These extracts are a rich source of phytochemicals which provides anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and anti-oxidant effects.
INDICATIONS:
Velvert Disc is intended to reduce local infections, catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSI), and skin colonization of microorganisms commonly related to CRBSI, in patients with central venous or arterial catheters.
Short peripheral I.V.: A peripheral venous catheter (PVC), peripheral venous line or peripheral venous access catheter is a short, flexible tube that is placed into a peripheral vein in order to access the veins to properly administer intravenous therapy such as medication fluids.
– Midline venous catheters: A midline venous catheter is an 8 – 12 cm tube which is inserted in the upper arm with its tip located just below the axilla (area under the joint where the arm connects to the shoulder).
– Central venous catheters (CVC): Also known as a central line, central venous line, or central venous access catheter, a CVC is a catheter placed into a large vein.
– Dialysis catheters: The hemodialysis catheter is a tunneled catheter placed under the skin of patients undergoing hemodialysis.
– Arterial catheters: It is a thin, hollow tube that is placed into an artery of the wrist, groin, or other location normally used to measure the blood pressure more accurately as compared to that measured by a cuff.
-Epidural catheters: It is a very fine plastic catheter placed through the skin into the epidural space in your spine.
-Other percutaneous devices.
Velvert Disc is an integrated I.V. dressing that combines infection reduction with site visibility, catheter securement, and breathability. It is also proven to reduce CRBSI and vascular catheter colonization by providing immediate and continuous antimicrobial protection.
Velvert Disc helps to keep the catheters in place with large securement tape strip and conforming keyhole notch. Its integrated design allows for easy and consistent application.
We @Dattmediproducts consider that CRBSI is a matter of concern at national & international levels. It is feasible and possible to reduce the occurrence of these infections as it is directly related to the adoption of safe practice and protocol compliance. With the help of an integrated herbal antimicrobial formulation in VELVERT-DISC, we are able to provide immediate and continuous antimicrobial protection.