Gluten is a protein found in grains primarily wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten allergies, like any other allergies, develop when our body’s immune system becomes over sensitive and overreacts to gluten.
It causes several digestive issues such as gassiness, bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. It is not essential that people with a wheat allergy will also be allergic to other grains. They may or may not be allergic.
Do You Know?
Wheat is listed among the top eight allergens in the world. As per information given in the Indian Express article, an “International Symposium on Wheat Related Disorders (ISWD) 2019” was organized in the Capital by the Celiac Society of India (CSI) from January 10-13, 2019 to create awareness about early diagnosis and management of the disease.
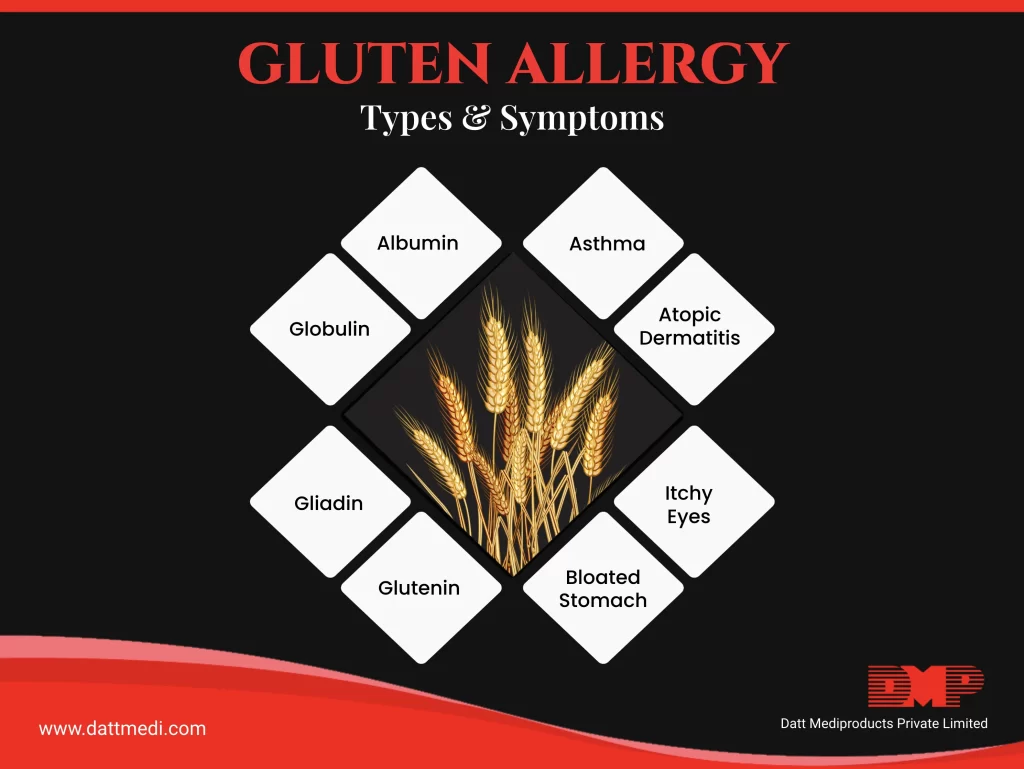
SYMPTOMS
Symptoms usually appear within a few minutes of consuming the wheat in any form. Symptoms can range from mild to severe life-threatening such as anaphylaxis.
– Nausea / Vomiting
– Stomach cramps/ abdominal pain, indigestion
– Diarrhea
– Irritation of your mouth and throat
– Hives and skin rashes
– Nasal congestion or runny nose
– Eye irritation
– Difficulty breathing, in most severe cases anaphylaxis may occur
TREATMENT
A Gluten or Wheat allergy is an IgE mediated allergic response. IgE antibodies get released against the Gluten Protein present in Wheat after being consumed by people allergic to it, triggering an immune response associated with several symptoms.
According to CELIAC INDIA, there are no biopsy changes with no damage to the intestines in people suffering from Wheat Allergy. The database also states that nearly 0.1% of the population is affected by this condition.
The only treatment method for wheat or gluten allergy is to follow a strict gluten/wheat free diet. Nowadays, several alternative grains are available even in the form of bread, pasta, cereals.
FOODS TO AVOID
The Gluten protein gives the dough texture and helps it to rise. People with gluten allergies must avoid the main grains and their preparations such as bread, cookies and biscuits, pasta, semolina-based products, couscous, and some beers.
Gluten may also be present in some non-obvious cereal-based products such as soups, salad dressings, marinades, seasonings, sauces, canned foods, and spices. The only thing is to do is to make sure that one reads food labels carefully to check the ingredients present. A gluten-free diet does not lack any major nutrients and is not inferior in any way to a gluten-containing diet.
FOODS SAFE FROM GLUTEN
People with gluten allergies should consume foods that are totally sure to not contain any gluten protein. These could be pulses, beans, rice, quinoa, fruits and veggies, oats, millet, flax, corn, chia potatoes, and soy along with plain meat, poultry, and fish products.
Although it may be difficult to live with a gluten allergy, it is not impossible. We @dattmediproducts recommend to consume any micronutrient supplements as asked by your allergist/ physician and follow a gluten-free diet to avoid any unwanted symptoms.
We also recommend people to not follow any special gluten-free diet unless diagnosed with the condition. This could make it difficult to confirm the diagnosis later on.
Stay Healthy, Eat Healthy..




