Peripheral artery disease (PAD) presents significant challenges to wound healing, affecting millions globally. This condition, characterized by narrowed arteries that reduce blood flow to the limbs, particularly the legs, not only causes discomfort and mobility issues but also complicates the natural healing process for wounds.
The Impact of PAD on Wound Healing
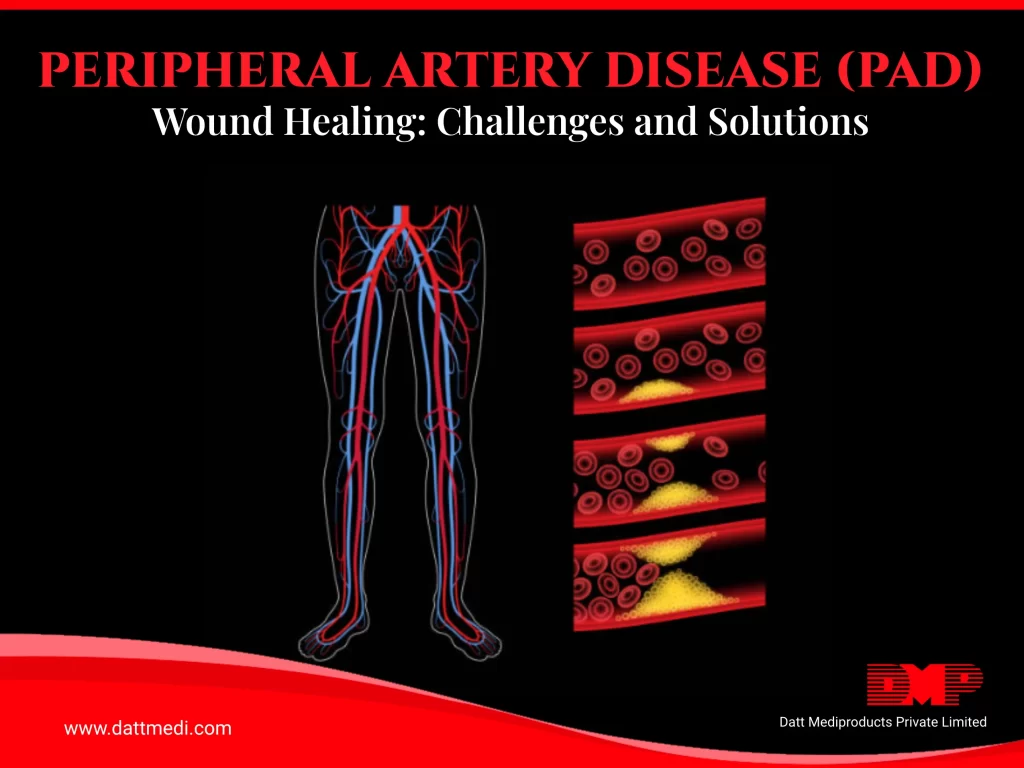
PAD restricts blood flow to tissues, depriving them of essential oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing. When individuals with PAD sustain wounds, reduced circulation delays the body’s healing mechanisms. Even minor cuts or abrasions can become chronic wounds, prone to infection and slow to heal. The diminished circulation also hinders the body’s ability to deliver immune cells and growth factors to the wound site, further complicating recovery.
Challenges Faced by Patients with PAD often experience:
1. Delayed Healing:
Wounds take longer to heal, increasing the risk of infection and complications.
2. Chronic Wounds:
Persistent wounds that do not heal properly, requiring prolonged treatment and care.
3. Risk of Amputation:
Severe cases may lead to tissue death (gangrene), necessitating amputation.
Specialized Wound Care Approaches: Managing wounds in PAD patients requires a specialized approach that addresses both the wound and underlying circulatory issues:
1. Improving Blood Flow:
Medical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery may restore blood flow to the affected area, enhancing wound healing.
2. Advanced Dressings:
Specialized dressings that promote moisture balance and provide infection barriers are crucial. For instance, alginate dressings for exuding wounds or hydrocolloid dressings for maintaining a moist environment can aid healing.
3. Compression Therapy:
Controlled compression helps improve leg circulation, reduce swelling, and promote better blood flow, facilitating wound healing.
4. Patient Education:
Empowering PAD patients to understand the importance of regular foot care, proper hygiene, and recognizing signs of infection can prevent complications and support healing efforts.
Peripheral artery disease significantly affects wound healing, necessitating a multidisciplinary approach involving vascular specialists, wound care nurses, and patient education. Addressing both vascular issues and wound management strategies can enhance outcomes for PAD patients, improving their quality of life and reducing complications.
Understanding these challenges and implementing specialized wound care approaches tailored to PAD patients is crucial for effective treatment and support.
For more information on our comprehensive range of wound care and advanced wound care products, please visit www.dattmedi.com.