Vascular access in surgical settings is virtually indispensable. The intravenous administration of fluids, medications, blood products and parenteral nutrition, whether peripherally or centrally, is a routine practice in healthcare setups.
The same has been documented in several medical journals such as The American Journal of Epidemiology and the Annals of Pharmacotherapy. According to which, up to 80% of hospitalised patients in recent medical practice receive intravenous therapy while they are admitted.
Peripheral intravenous cannulation (PIVC) is the most widely used method for intravenous therapy. Although insertion of cannula and subsequent intravenous therapy are generally well tolerated, complications may arise that may lead to a prolonged hospitalisation. These complications may include Catheter-related bloodstream infections (CR-BSI), Bruising & vein irritation or Blockage.
Fact:
Epidemiological studies from Europe and US region indicate the incidence of CR-BSI as a percentage of catheters inserted, is between 3% and 7%. (Infections caused by intravascular devices used for infusion therapy: pathogenesis, prevention and management. In: Bison AL, Waldvogel FA, eds. Infections associated with medical devices. Washington DC: ASM Press, 1994:155–205.)
It is vital to understand that any procedure that punctures the skin comes with a risk of associated infections. Since IV sits directly in your bloodstream, a regular observation of the IV site and strict procedures to prevent infection must be practiced by the nursing staff. These will include maintaining good aseptic techniques to minimise the risk of local and systemic infections.
The CDC Guidelines:
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have issued certain Guidelines For The Prevention Of Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections. These have been developed for healthcare personnel who insert intravascular catheters and for persons responsible for surveillance and control of infections in hospital, outpatient, and home healthcare settings.
These guidelines include Selection of Catheters; Hand Hygiene & Aseptic Techniques; Maximal Sterile Barrier Precautions; Skin Preparation; Catheter Site Dressing Regimens; Cleansing; Catheter Securement Devices etc.
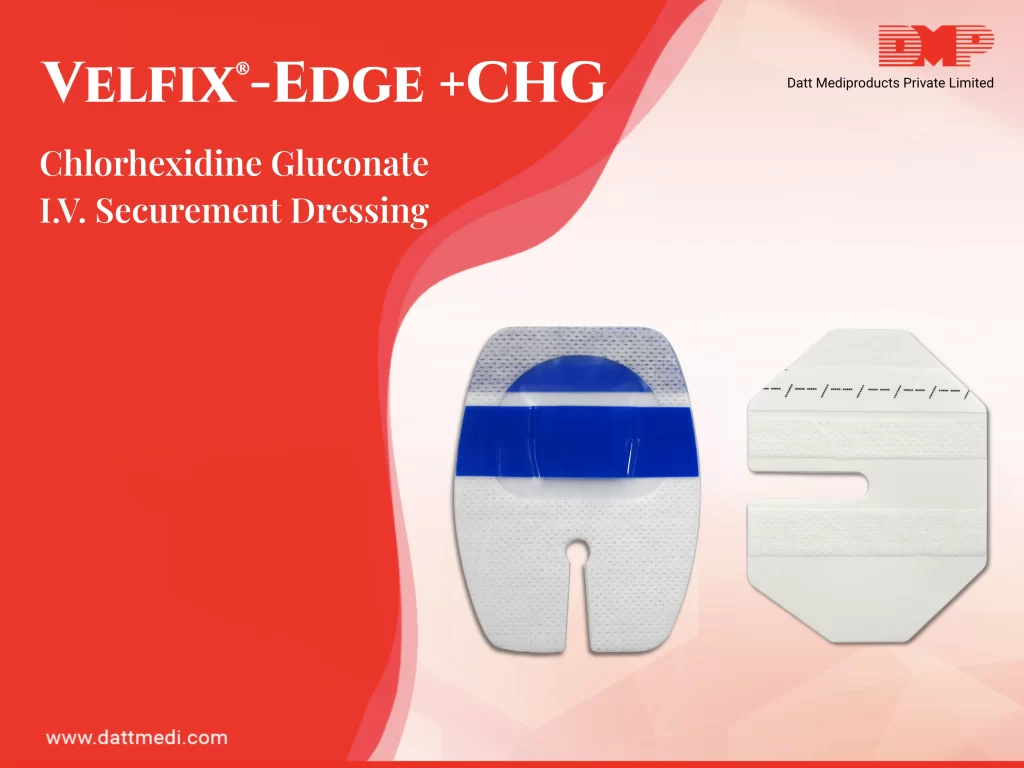
- It is recommended to prepare a clean skin with an antiseptic (70% alcohol, tincture of iodine, an iodophor or chlorhexidine gluconate) before peripheral venous catheter insertion.
- The use of either a sterile gauze or sterile, transparent, semipermeable dressing to cover the catheter site are recommended.
- It is also suggested to monitor the catheter sites visually when the dressings are changed or by palpation through an intact dressing on a systematically, depending on the clinical situation of each patient.
We have introduced a high utility, highly effective IV Cannulization dressing kit specially designed to take care of insertion & dressing change of peripheral vascular devices.
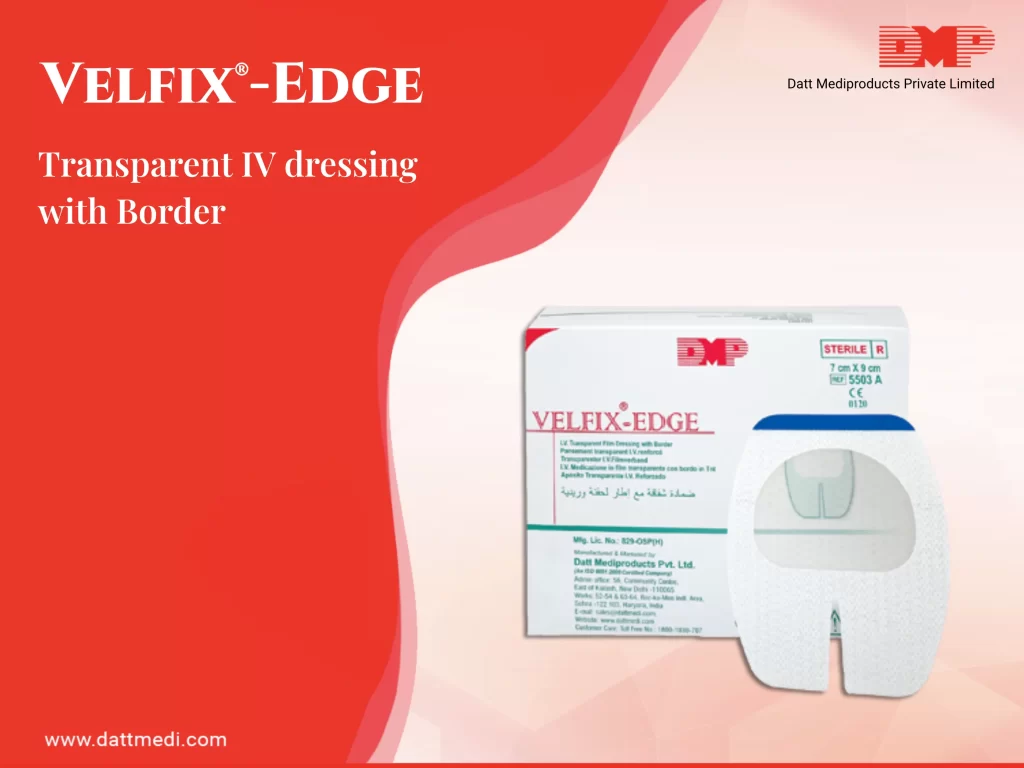
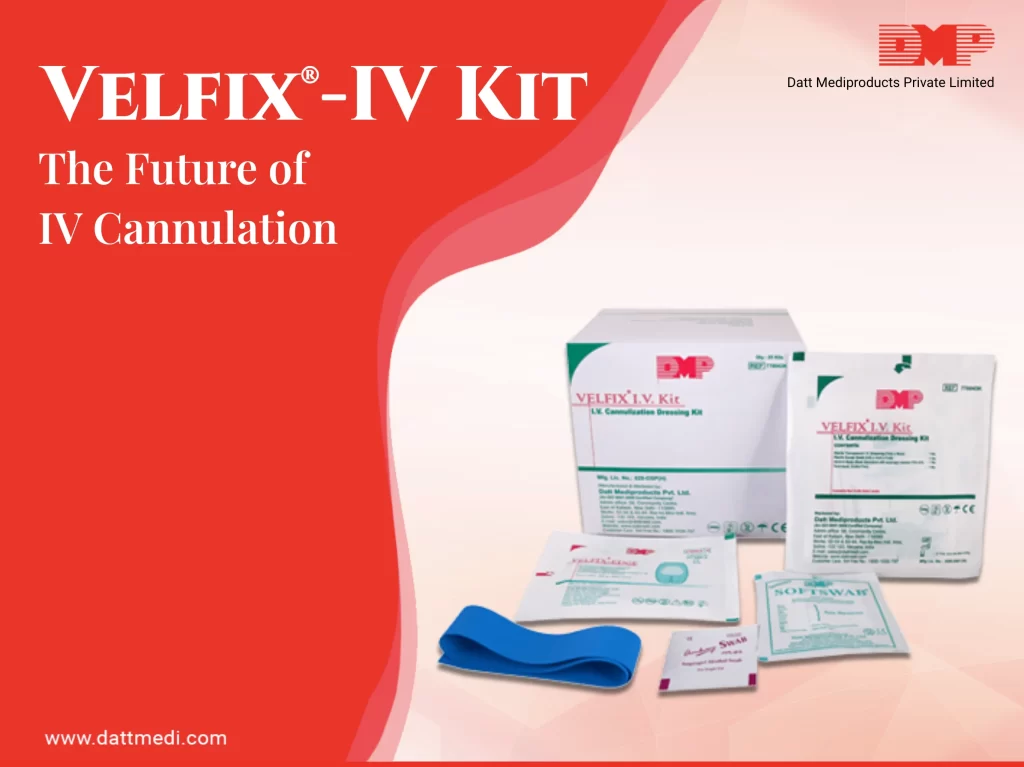
VELFIX®-IV KIT
A sterile IV Dressing Kit for cannula fixation, including 4 contents in accordance with CDC guidelines.
- Tourniquet: The kit comes with a latex free tourniquet which helps to identify the veins. Since it is a non-reusable tourniquet, there are a reduced chances of cross- contamination due to carrier property of Velcro tourniquets and thereby preventing skin allergy.
- Antiseptic Swab: A 70% IPA Swab/chlorhexidine gluconate CHG swab is included in the kit which is considered ideal for skin preparation before peripheral venous catheter insertion. This falls under Category 1B as per Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) implying strong recommendation for implementation, supported by some experimental, clinical, or epidemiologic studies, a strong theoretical rationale; or an accepted practice supported by limited evidence.
- Velfix® -Edge IV Dressing (7cm x 9cm): Transparent IV dressing with Window Frame delivery design to allow continuous observation of the IV site while providing better seal around the catheter with stabilization non-woven boarders. The notched design ensures effective stabilization of the catheter. The transparent film of the dressing serves as a waterproof sterile barrier to external contaminants. The film is breathable in nature providing high MVTR with an effective wear time of up to 7 days. The dressing comes with a hypoallergenic, latex-free adhesive that is gentle to the skin yet holds catheter in place. It offers single hand application & gentle removal.
The Sterile Gauze Swab of the Velfix® -I.V. Kit is available to control the back flash of blood.
We Datt Mediproducts understand that catheter stabilization is imperative to decrease the risk for phlebitis, catheter migration and dislodgement, and potentially in preventing CR-BSIs. Velfix-IV Kit is an effective and high utility securement device which avoids disruption around the catheter entry site and may reduce the degree of bacterial colonization also.