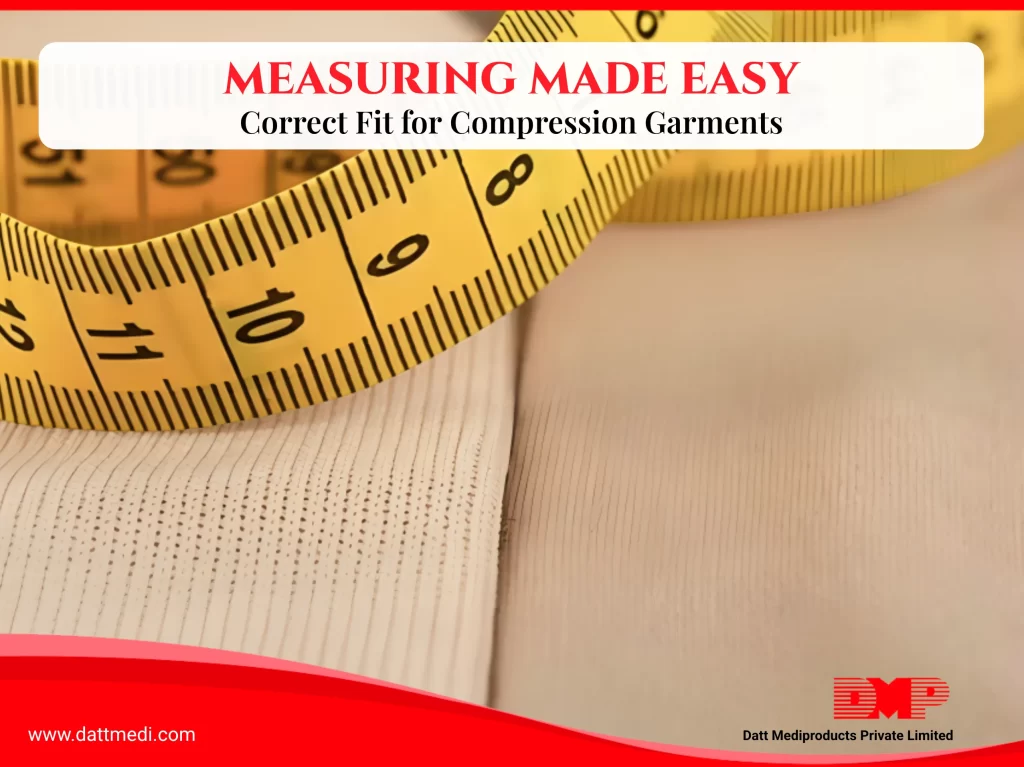
A well-fitted compression garment supports movement, reduces swelling, and improves overall comfort during recovery. Even small measurement errors can affect its effectiveness. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, clinician, or distributor, understanding how to measure compression garments correctly ensures safe therapy and reliable results.
For suitable options, check our Compression Stockings Collection.
1. Why the Right Measurement and Fit Matters
Compression garments apply controlled pressure along the limb. The correct size ensures even pressure distribution and therapeutic effectiveness.
Benefits of Proper Fit:
- Reduces swelling and discomfort
- Improves blood and lymph circulation
- Supports healing after injury, surgery, or chronic conditions
- Makes daily activities like walking, standing, or sitting more comfortable
Example: Someone managing mild swelling or early varicose veins often feels lighter and more supported when using a properly sized garment, following a reliable compression stocking size guide.
2. Tools You Need for Accurate Measurement
Accurate sizing doesn’t require advanced tools.
You need:
- A soft measuring tape
- Manufacturer’s compression measurement chart or sizing guide
- Notebook or phone to record values
- Mirror or assistance for hard-to-reach areas
- Good lighting for accurate readings
These simple tools help follow a medical compression garment sizing guide and reduce measurement errors.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Measure Correctly
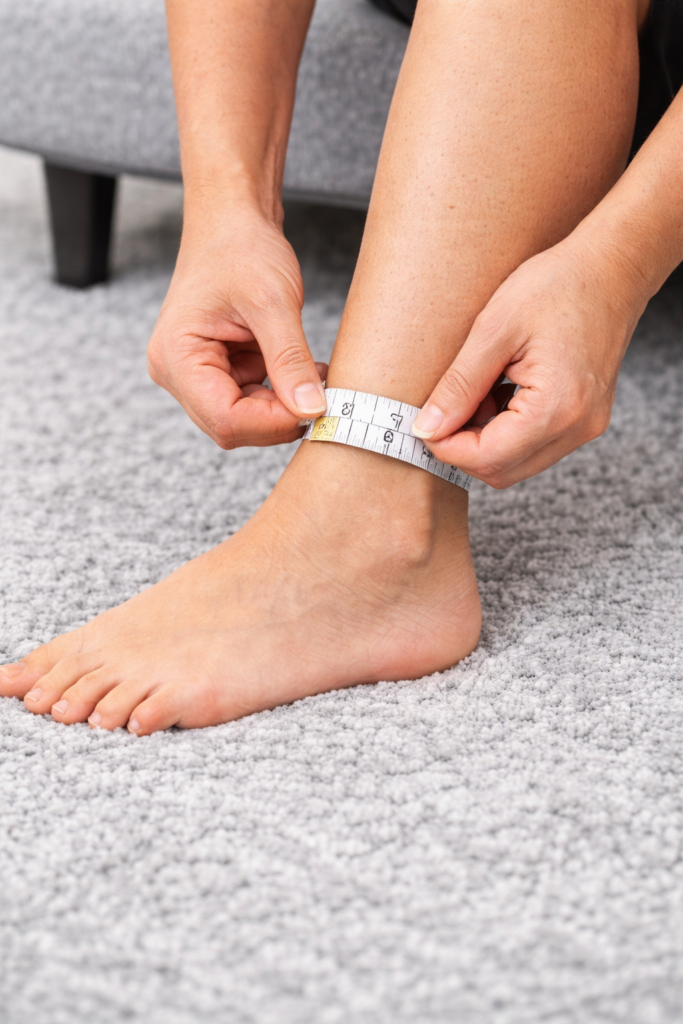
i) Ankle: Measure the narrowest point above the ankle bone.
ii) Calf: Measure the widest part of the calf for proper fit and support, including wide-calf users.
iii) Thigh (for thigh-high garments): Measure the thickest part of the thigh to avoid rolling and ensure secure fit.
Leg Length:
- Knee-high: heel to just below the knee crease
- Thigh-high: heel to the top of the thigh

iv) Arms (for sleeves/supports): Measure wrist, forearm, upper arm, and arm length. This ensures smooth, even compression from wrist to shoulder.
Quick Tips:
- Measure early in the morning when swelling is minimal.
- Sit comfortably, keep tape snug, measure twice, and avoid measuring over clothes.
4. Common Fitting Mistakes to Avoid
- Too Tight: Can cause numbness, tingling, or deep marks.
- Too Loose: Slipping or wrinkling reduces effectiveness.
- Incorrect Length: Too short rolls or digs in; too long bunches or slides down.
- Not Rechecking: Limb size changes due to swelling, healing, or weight changes—regular measurement is important.
For reference, see our Compression Stockings Size Chart India.

5. When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Specialists can confirm the correct compression level and ensure measurements match your condition, especially after surgery or for vascular issues.
Consult if you notice:
- Persistent or increasing swelling
- Discomfort while wearing the garment
- Size falling between two chart options
- Post-surgical changes
- Conditions like diabetes or vascular disorders
Professional guidance ensures safe and effective therapy, particularly when using compression garments for varicose veins.
Accurate measurements are the foundation of effective compression therapy. Using simple tools, careful technique, and a trusted compression stocking size guide ensures your garment fits comfortably and supports healing. When unsure, consulting a healthcare professional provides confidence and safer results.