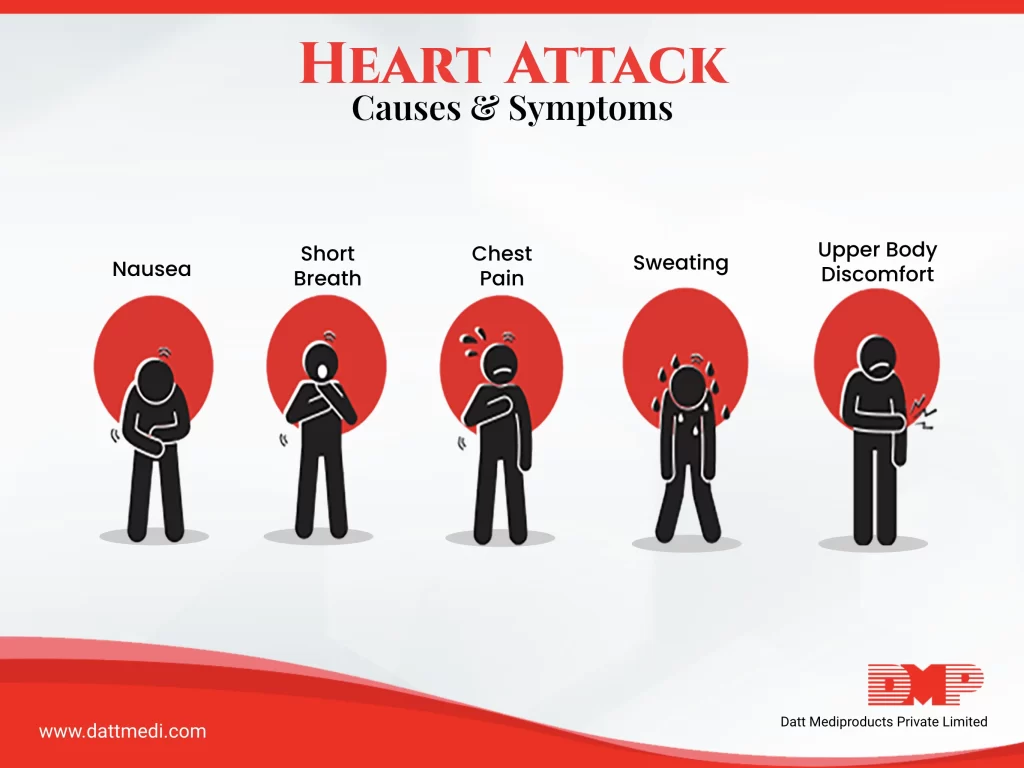
Don’t wait to get help if you experience heart attack warning signs. Some heart attacks are sudden and intense. But most start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort. Pay attention to your body.
A heart attack is a frightening experience. If you have experienced a heart attack, or are close with someone who has, you should know this: You are not alone. In fact, tens of thousands of people survive heart attacks and go on to lead productive enjoyable lives.
Do you know – The heart is one of the largest muscles in the body.
What happens during a heart attack?
The heart’s main function is to pump blood throughout the body; supplying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs and removing the deoxygenated blood. The blood is supplied to the heart by a network of arteries that surround it.
A heart attack occurs when there is a clot in one of the main arteries blocking the heart from getting blood and thus oxygen, causing the heart muscle to get damaged.
One of the most common causes of a heart attack is coronary artery disease. This is when, over a period of time, the artery starts to become narrower due to a build-up of cholesterol or fatty deposits on the lining of its inner wall. It constricts the blood flow to the heart causing it to pump that much harder.
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) is the medical name for a heart attack.
What are common symptoms of Heart Attack?
Every organ needs oxygen-carrying blood to stay alive, and the myocardium is no exception. Usually, heart attack victims feel some symptoms in the days leading up to the attack. These symptoms are usually much more severe and longer lasting.
Most common among are:
– Chest pain – One can feel tightness, pressure, pain, and a “squeezing” feeling in the chest. The pain can also be felt in the back, jaw, shoulder, or especially the left arm.
– Shortness of breath – The heart rate speeds up and starts to beat irregularly.
Other symptoms of heart attack may or may not develop:
– Anxiety – Constant worrying or anxiety that is not related to a specific stressor in your life should be addressed. You may have trouble falling asleep at night, or you may wake up in the middle of the night plagued by anxiety or feelings of doom and distress.
– Cold Sweating – Breaking out in a cold sweat for no obvious reason could signal a heart attack.
– Nausea and Vomiting -Nausea, indigestion, vomiting, or a feeling of fullness that lasts for more than a few days may not be related to your stomach. When oxygen-rich blood is not moving through your circulatory system, the body may respond by sending pain signals to the abdomen.
– Indigestion, Heartburn & Lightheadedness or extreme fatigue
Factors associated with an increased risk of a heart attack
1. Age: Heart attacks are more likely when a man is over 45, and when a woman is over 55.
2. Diabetes: This can increase heart attack risk.
3. Diet: For example, consuming large quantities of saturated fats can increase the chances of coronary artery disease.
4. Genetics: If heart problems run in your family then it increases the risk of getting a heart attack
5. HIV: People who are HIV-positive have a 50 percent higher risk.
6. High cholesterol levels: Increase the chance of build-up on the arteries wall that leads to less blood supply to the heart.
7. Hypertension: High blood pressure can put unnecessary strain on the heart.
8. Obesity: Being significantly overweight can put pressure on the heart causing it to work much harder.
9. Smoking: Smokers are at much higher risk than non-smokers as smoking damages the lining of the arteries.
10. Stress: Being stressed elevates certain hormones that can lead to higher levels of blood pressure and cholesterol levels that increase the risk of heart attacks. There are also studies being done on how chronic stress can change the way your body clots blood.
11. Physical inactivity: is a factor in heart attack risk. Physical activity has shown to lower blood pressure.
A healthy, stress-free life is the ultimate key to prevent heart attacks and cardiac diseases. Meditation, yoga, eating right, helps to lower your blood pressure and keep yourself fit. Even in your work day just taking a 10-minute break every once in a while to relax and de-stress yourself helps.
Everything you eat, the routine you keep for yourself matters in the prevention of heart attacks. Try adding a half an hour workout session 3 times a week. Or if that seems too much initially start by just taking the stairs or taking a stroll. Changes can start small.