Its okay to cross check whether some work has been done or not, to avoid any unwanted circumstances. But when these repetitive thoughts & actions take over and interfere with your daily life causing distress it may be OCD.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is an anxiety disorder characterized by uncontrollable, reoccurring thoughts and behaviors. Recurring thoughts are obsessions and behaviors are compulsions. There is an urge to repeat over and over.
- OCD is a mental health disorder. - OCD is chronic in nature. - OCD can affect people of all ages and walks of life. As per the National Health Portal (Govt. of India), the lifetime prevalence of OCD in general population is 2-3%. - Men and women can be affected equally. OCD occurs when there is a vicious cycle of “Obsessions and Compulsions”. - The thoughts are distressing, intrusive & obsessive - The actions are repetitive, compulsive, physical or mental. - OCD is a treatable disorder. - Treatment options include Psychotherapies like Exposure & Response Prevention (ERP) and Medications. - OCD is often concomitant with other disorders like Depression, Social Phobia and Tourett’s disorder.
SYMPTOMS
People with OCD may have the symptoms of Obsessions, or Compulsions or both. OCD symptoms interfere in normal day to day functioning such as work, school, and personal relationships.
1. What are Obsessions: Obsessions are recurrent thoughts, mental images, urges or impulses which are outside of a person’s control and often cause anxiety.
2. What are Compulsions: Compulsions are repeated rituals, behavior or mental acts which are done in response to an obsessive thought.
3. Compulsions are often aimed to neutralize or counteract the anxiety caused by Obsessions. These may include avoiding situations that trigger obsessive behaviors and thoughts.
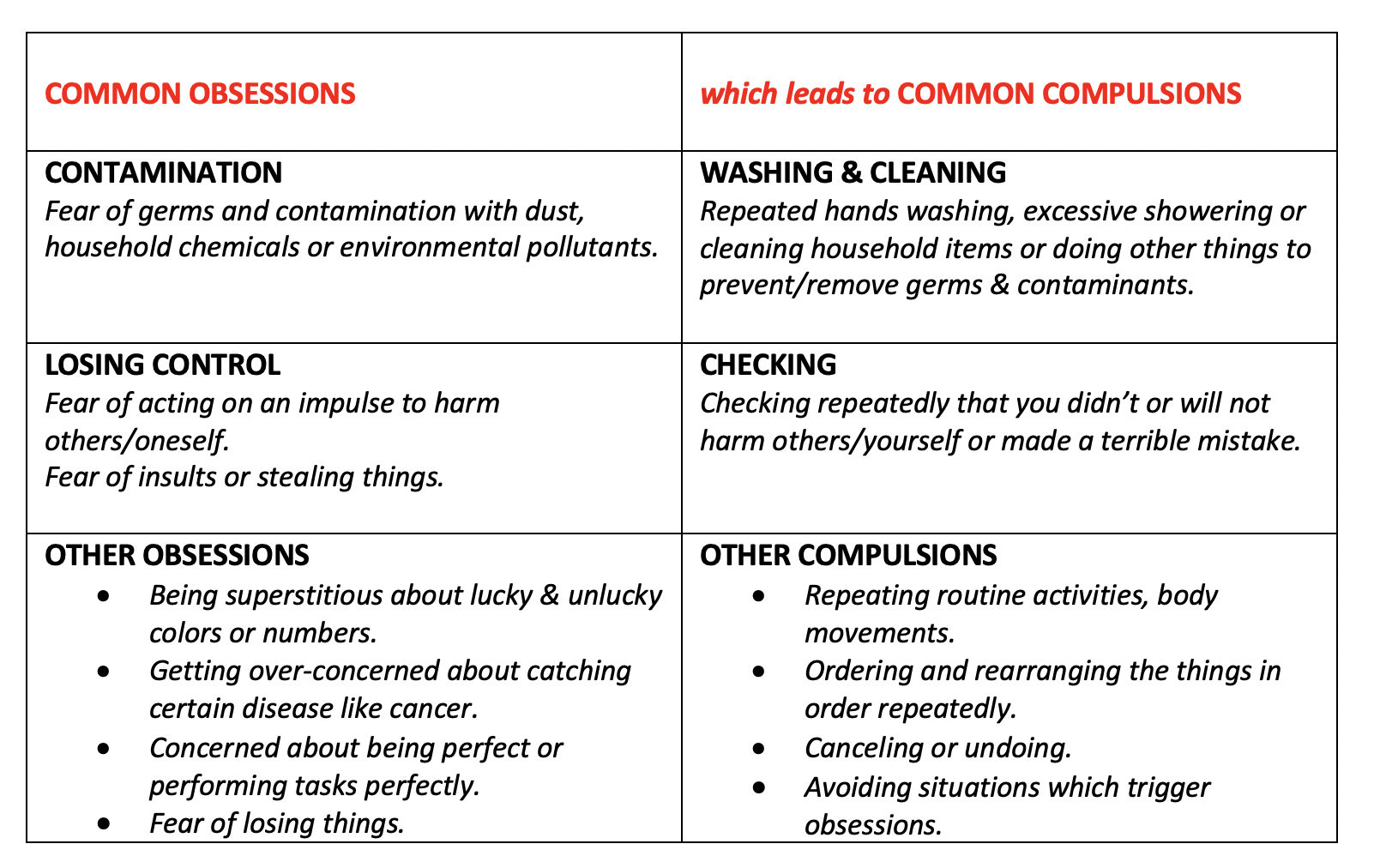
As per the International OCD Foundation, following are a few of the common examples of Obsessions and Compulsions in OCD:
Effective Treatment Modalities of OCD:
1. MEDICATIONS: OCD medications include Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) which help reduce OCD symptoms. SSRIs may take from 8 to 12 weeks to start working with rapid improvement shown in some of the patients.
2. PSYCHOTHERAPY: Treatment with psychotherapies is usually personalized and might begin in combination to the medications. An example of psychotherapy includes Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) with Exposure & Response Prevention (ERP) being one of the major types. These therapies include spending time in situations triggering compulsions but then being prevented from undertaking the usual compulsion acts.
We @DattMediproducts understand that OCD symptoms are recognized by the patients who get further distressed because they are not being able to stop or control them. They get caught in the vicious cycle of Obsessions & Compulsions as their symptoms consume a lot of their daily time affecting them emotionally, socially, and financially. Since OCD is treatable, we recommend seeking professional help as soon as possible.