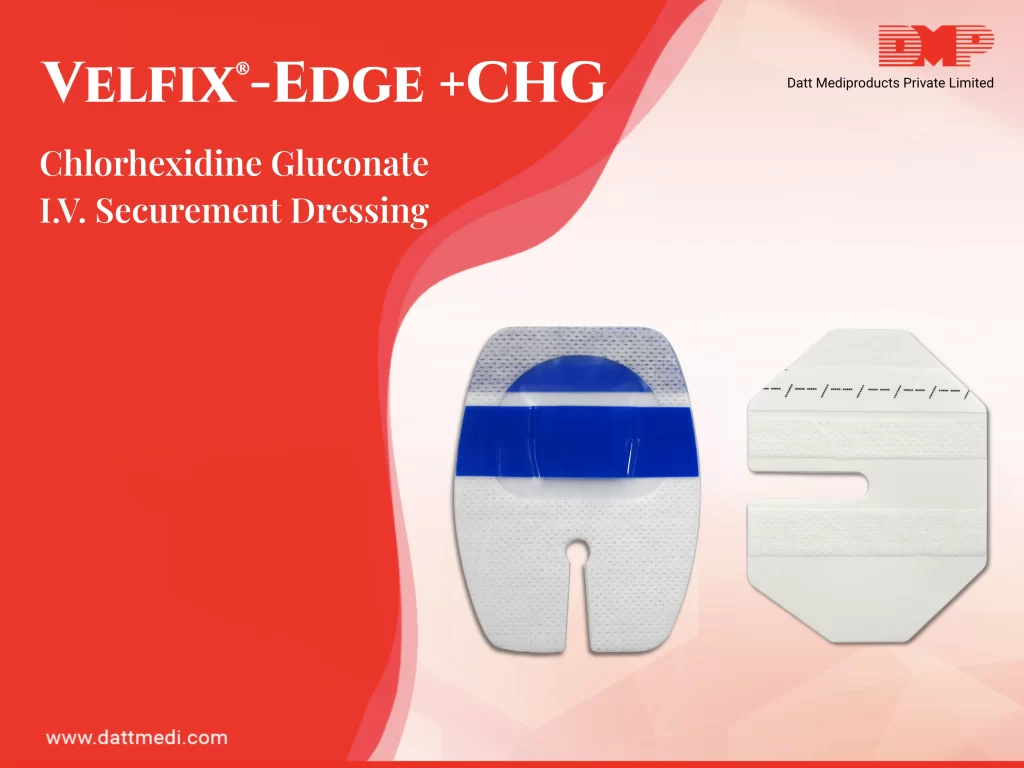
Proper wound care is essential for facilitating the healing process and preventing complications. Whether it’s a minor cut or a more severe injury, following the right dos and avoiding the don’ts can significantly contribute to better healing.
In this blog, we will explore key practices to ensure optimal wound care.
Dos:
Keep the Wound Clean:
It is crucial to clean the wound gently using mild soap and water. Additionally, consider using a saline solution for cleaning when necessary. A clean wound reduces the risk of infection and promotes a faster healing process.
Use Appropriate Dressings:
Selecting the right dressing based on the type and severity of the wound is vital. Changing dressings regularly, as advised by healthcare professionals, helps maintain a sterile environment and supports the healing process.
Promote Moist Healing:
Create a moist environment conducive to healing. Using gauze or appropriate dressings can help keep the wound moist, facilitating cell growth and minimizing scarring.
Monitor and Seek Medical Advice:
Regularly monitor the wound for any signs of infection or complications. If redness, swelling, or increased pain occurs, seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention can prevent further complications.
Maintain a Healthy Diet and Hydration:
A balanced diet rich in nutrients is essential for the body’s healing process. Adequate hydration supports overall recovery. Ensure that the body receives the necessary vitamins and minerals for optimal wound healing.
Don’ts:
Avoid Harsh Cleaning Agents:
Refrain from using harsh chemicals or alcohol-based solutions on the wound. Hydrogen peroxide should be avoided, as it can impede the natural healing process.
Don’t Pick at Scabs or Wounds:
Resist the temptation to pick at scabs or peel off healing tissue. Allowing the body’s natural healing process to take place without interference is crucial for proper wound healing.
Don’t Apply Excessive Pressure:
Avoid applying excessive pressure or using tight bandages that may impede blood circulation. Dressings should be snug but not constricting to promote proper healing.
Don’t Ignore Signs of Infection:
Ignoring signs of infection, such as increased pain, pus, or foul odour, can lead to severe complications. Seek medical attention promptly if any of these signs appear during the healing process.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Drinking:
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can hinder the body’s ability to heal effectively. To support the healing process, it is crucial to avoid these habits during recovery.
By following these wound care dos and avoiding the corresponding don’ts, individuals can contribute to better healing outcomes. Remember, seeking professional medical advice for any concerns or signs of infection is always a prudent step in the journey to recovery.
For more such tips and information, follow us at @dattmediproducts or visit www.dattmedi.com/woundcare