Minor scratches, scrapes, and cuts are a part of our everyday life. When our skin is injured, our body works to heal the wound. No two wounds are the same and thus different wounds require different attention and care.
Healing is delayed when wounds become infected with harmful microorganisms. If left untreated, there is a risk of the infection spreading to other body parts.
Dermatologists recommend the following guidelines to care for minor cuts and scrapes:
Wash your Hands: The first step in the First Aid process is to wash your hands with soap and water to avoid any infection.
Stop the Bleeding: Applying a gentle pressure with a clean cloth or gauze. Elevating the wound also helps to stop the bleeding.
Clean the Wound: Cleaning the wound is a crucial step to remove dirt and debris. Rinse the wound under running water and wash around the wound with
water and soap. But make sure none of the soap comes in contact with the wound.
Apply petroleum jelly or an Antibiotic: This step helps to keep the wound area moist and prevents the spread of dirt and microorganisms.
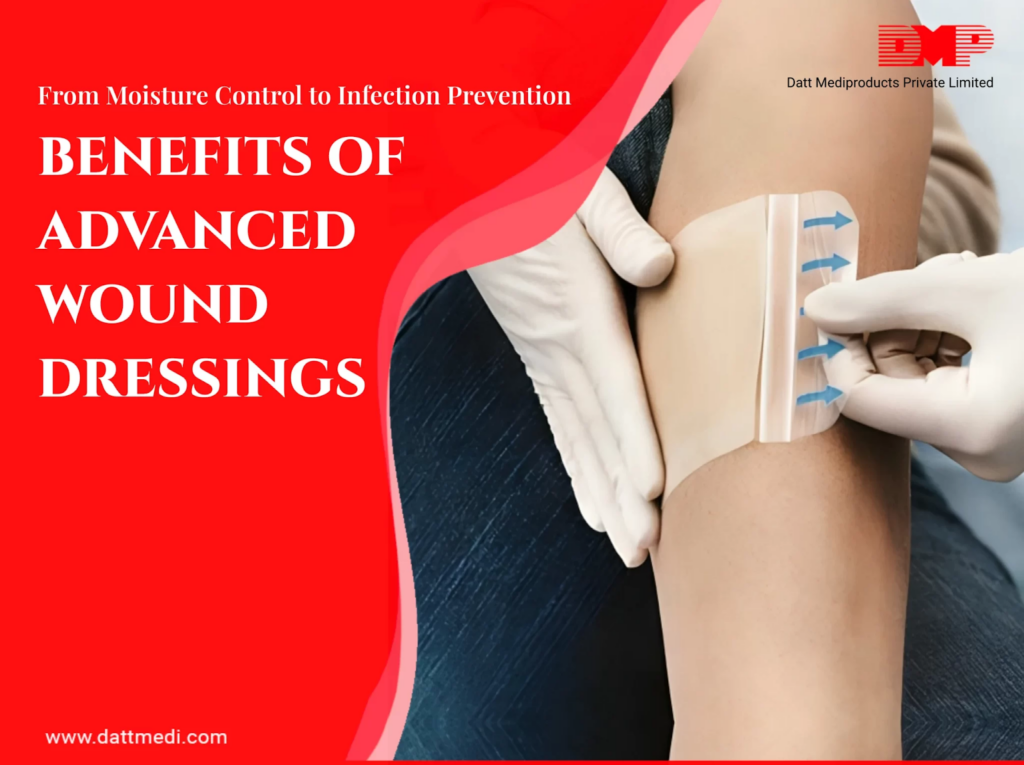
Cover the Wound with Sterile Dressings: Covering the wound with a sterile dressing or gauze helps to keep it clean and protects it from outside contaminants. These dressings should be changed regularly to keep the wound clean.
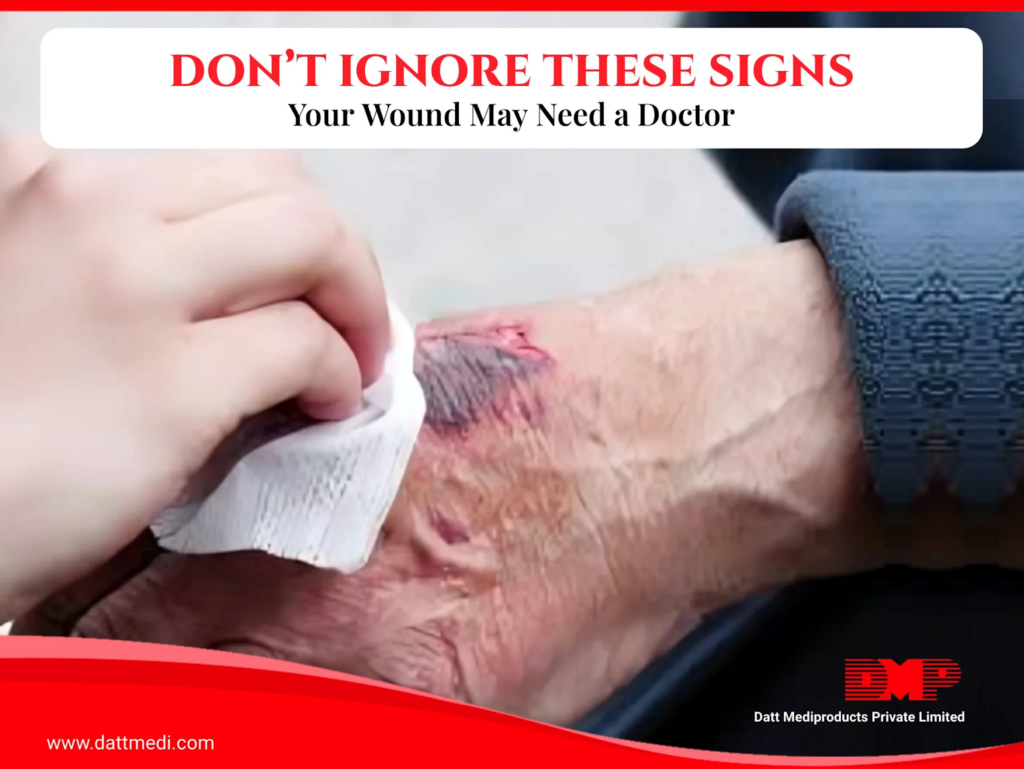
Look for any signs of Infection: A wound that isn’t healing normally may be dark in color or have red streaks and increasing pain. If the wound isn’t healing it is advisable to go to a doctor to get it checked up.
Tip- Make sure you get a tetanus shot if your wound is from a dirty or rusty object.
Signs of infection and when to see a clinician*
Initially, some mild redness directly around the wound is a normal part of healing, but seek medical care if there is any of the following:
– Redness spreading out or “streaking” from the wound
– Increased pain or swelling of the wound
– Difficulty moving the affected area
– Pus or odorous wound drainage
– Warmth around the wound site
– Fever higher than 100.4 degrees
– Any concerns about poor healing, large or gaping wounds, bite injuries, etc.
Wound Healing Complications
Infection: Infection is the most common cause of delayed wound healing. A localized infection, if not controlled, can eventually spread to the bloodstream (systemic infection) resulting in sepsis, leading to multiple organs dysfunction, and subsequent life- and limb-threatening infection.
Osteomyelitis: Infections can travel through the bloodstream or by spreading from nearby tissue. When the infection reaches the bone it is referred to as Osteomyelitis. 20% to 60% of the patients suffering from Diabetic Foot Ulcers have underlying Osteomyelitis that increases their risk of lower extremity amputation.
Tissue Necrosis & Gangrene: Ulceration and Gangrene may occur in the lower extremities due to poor blood supply because of peripheral vascular diseases. A wet and draining necrotic tissue may result in hospitalization and amputation.
Peri-wound Maceration: Chronic wound exudates often consist of substances, which damage the skin surrounding the wound area. The damaged skin looks pale/ white and wrinkled. This is called maceration and affects the skin in the peri-wound area. It can prevent the wound from closing and healing.
EDEMA: Edema is the excess fluid trapped in the body’s tissue that leads to swelling. Mild edema dissipates by itself, but severe edema may slow the healing process because it compresses the blood vessels in the affected area leading to further complications like pain, stiffness, motility issues, decreased microcirculation, increase the risk of infection, peri-wound skin damage etc.
Apart from these, there may be many other complications too. Comorbid conditions such as malignancies or diabetes, also need to be managed. The underlying causes resulting in the poor healing of chronic wounds may also include malnutrition, arterial insufficiency, infection, age, obesity, the weak immune system to name a few.
The risk factors and complications of a chronic non-healing wound should be identified and appropriately managed by a clinician. The complications deteriorate the condition and increase the cost to the patient both financially and personally. It affects a patient’s quality of life and may contribute significantly to their morbidity and mortality.
An early detection and management of the risks and taking appropriate treatment by consulting a professional expert/clinician can help to mitigate further complications and achieve a positive outcome by better wound healing.
We @ Datt Mediproducts Pvt. Ltd. manufacture a range of wound healing products with impeccable quality by following international standards.