Discover Informative Blogs on Healthcare Solutions
Search by Blog
Read by Category
Patient Care Solutions
Health & Wellness
Environmental Health
First Aid & Emergency Care
Advance Wound Care
Wound Care
Your healing journey continues beyond this blog
Find the right products for better recovery at online store


Wound healing is often slowed when the body cannot efficiently move blood and excess fluid away from the affected area. This causes low blood flow which leads to reduced oxygen & nutrient supply, both are critical for cell repair. This is frequently seen in chronic venous ulcers, lymphedema, diabetic wounds, and post-surgical swelling.
Compression therapy is one of the most effective clinical methods to improve circulation, support healing, and enhance overall wound management.
By applying controlled and consistent pressure, compression therapy reduces fluid buildup, improves oxygen delivery, and creates a stable environment that promotes faster tissue repair.
What Is Compression Therapy? How It Works
Compression therapy uses medical tools such as compression bandages, garments, or dressings to apply even pressure to a limb or wound site. This helps to:
- Redirect blood flow toward the heart
- Reduce fluid accumulation under the skin
- Improve oxygen supply to damaged tissues
- Support formation of healthier new tissue
This controlled pressure creates a stable, balanced healing environment and reduces strain on surrounding skin.
Types of Compression Therapy
1. Elastic Compression Bandages
Widely used for venous ulcers and chronic wounds because they allow adjustable pressure and support daily wound care.
Related Product: Compression Bandages – Wound Care Range
2. Compression Garments
Ideal for long-term swelling, lymphedema care, and post-surgical recovery. They offer uniform pressure and help maintain inflammation control. Velcare® Varicose Vein Stockings– Compression Garments

Know More About – Velcare® Varicose Vein Stockings- Compression Garments
3. Dressings With Built-In Mild Compression
Foam and hydrocolloid dressings provide gentle compression while maintaining moisture balance. Recommended options:
- Velfix® Foam Dressings – Advanced Wound Care
- Velsoft® Silicone Foam Dressings – Advanced Wound Care
- Velvert® Advanced Dressings – Antimicrobial & Moisture Management
How Compression Therapy Supports Wound Healing
- Improved Blood Flow – Prevents blood pooling and delivers oxygen and nutrients for efficient tissue repair.
- Swelling Control (Edema Management) – Removes trapped fluid, reducing discomfort and creating a stable environment.
- Enhanced New Tissue Formation – Supports orderly tissue repair and faster wound closure.
- Reduced Risk of Raised Scars – Mild compression after surgery or burns helps prevent thick or raised scars.
When Compression Therapy Is Recommended
- Chronic Venous Ulcers – Supports circulation and long-term healing.
- Lymphedema Care – Manages fluid buildup, heaviness, and infection risk.
- Post-Surgical Recovery – Controls inflammation, stabilizes the wound area, and supports smoother healing.
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers – Can support healthy circulation under clinical guidance.

Read more about Compression Therapy
Benefits of Compression Therapy
- Faster wound healing through improved circulation
- Reduced risk of recurrence, especially in venous ulcers
- Lower pain and discomfort due to decreased swelling
- Better mobility and overall patient comfort
How to Use Compression Therapy Safely
- Ensure Proper Fit – Pressure must match clinical needs; too little is ineffective, too much can cause skin damage.
- Monitor the Skin Regularly – Watch for numbness, tingling, coldness, or unusual pain.
- Increase Pressure Gradually – Start with lower compression levels and increase slowly under clinical supervision.
When Compression Therapy Should NOT Be Used:
Avoid compression unless recommended by a clinician if the patient has:
- Poor arterial circulation
- Active infection at wound site
- Acute heart failure
- Severe peripheral arterial disease (ABI)
Always consult a healthcare professional before beginning or modifying compression therapy.
Best Practices for Better Healing
Compression works best when combined with:
- Gentle wound cleansing
- Moisture-balancing dressings (foam, antimicrobial)
- Adequate nutrition (protein, vitamins, minerals)
- Regular assessments by wound-care specialists
Together, these steps create a complete, supportive healing environment.
Compression therapy is vital for accelerated wound healing, edema control, venous ulcer management, lymphedema care, and post-surgical recovery. When combined with appropriate dressings and monitored safely, it offers faster healing, improved patient comfort, and reduced risk of complications or recurrence.
Explore Professional Wound-Care Solutions – Wound Care Category

Nutrition plays a central role in wound healing, often as important as medical care itself. When the body sustains an injury, foods for wound healing become essential as its demand for specific nutrients increases.
The right foods can help accelerate tissue repair, reduce inflammation, strengthen the immune system, and enhance overall recovery. This blog explores scientifically backed foods for wound healing that actively support faster and more effective recovery.
Phytonutrient Power for Tissue Repair
What they are:
Phytonutrients are bioactive compounds in plants, such as flavonoids and carotenoids.
Why they matter:
Wound sites often experience oxidative stress due to free radicals, which can delay healing. Phytonutrients neutralize these free radicals, creating a favorable environment for tissue regeneration.
Food sources:
- Berries (flavonoids): Blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries reduce oxidative stress.
- Sweet potatoes & carrots (carotenoids): Support cell growth and boost skin barrier function.
Quick Tip: Including a cup of mixed berries in breakfast or roasted sweet potato as a side dish provides antioxidant protection during recovery.
Collagen-Activating Foods
What they are:
Nutrients that directly stimulate collagen synthesis.
Why they matter:
Collagen forms the structural framework of new tissue and strong scar formation.
Key nutrients & foods:
- Vitamin C (bell peppers, citrus, kiwi): A co-factor in collagen production.
- Copper (sunflower seeds, cashews, lentils): Supports the cross-linking of collagen fibers for durability.
Quick Tip: A salad of bell peppers, spinach, and sunflower seeds supplies both vitamin C and copper—maximizing collagen activation.
Gut Health and Healing Connection
What it is:
The gut microbiome plays a central role in nutrient absorption and immune regulation.
Why it matters:
Without a healthy gut, even the best diet cannot deliver full healing benefits. Probiotics strengthen the microbiome, enhance nutrient uptake, and improve immune defenses against infection.
Food sources:
Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, miso.
Quick Tip: Consuming a serving of probiotic yogurt daily can improve nutrient bioavailability, indirectly accelerating wound recovery.
Anti-Inflammatory Spice Cabinet
What they are:
Natural spices with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
Why they matter:
Chronic inflammation around a wound can slow tissue regeneration. Certain spices actively reduce inflammatory responses while fighting harmful microbes.
Food sources:
- Turmeric (curcumin): Reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Ginger: Enhances circulation and reduces swelling.
- Garlic: Provides antimicrobial support against infections.
Quick Tip: Adding turmeric to curries, ginger to tea, and garlic to meals integrates these benefits naturally into daily cooking.
Zinc Synergy Foods
What it is:
Zinc is essential for cell division and repair, but its efficiency increases when paired with vitamin C.
Why it matters:
Zinc deficiency can delay wound closure. Pairing zinc with vitamin C optimizes collagen production and tissue healing.
Food sources & pairings:
- Pumpkin seeds + oranges
- Chickpeas + bell peppers
This nutrient synergy ensures better absorption and function.
Iron-Rich for Oxygen Delivery
What it is:
Iron is critical for hemoglobin formation.
Why it matters:
Adequate hemoglobin ensures oxygen supply to regenerating tissues, which is vital for energy production during healing.
Food sources:
- Heme iron (easily absorbed): Red meat, chicken, fish.
- Non-heme iron: Lentils, spinach, fortified cereals.
Quick Tip: Pairing spinach (iron) with tomatoes (vitamin C) improves absorption, ensuring more oxygen reaches healing tissues.
Hydration Beyond Water
What it is:
Cellular hydration requires more than water—electrolytes are equally vital.
Why it matters:
Dehydrated cells cannot repair efficiently. Electrolytes maintain fluid balance, nerve signaling, and nutrient transport.
Food sources:
- Coconut water: Natural electrolytes.
- Watermelon & cucumbers: High water content plus minerals.
- Broths & soups: Provide both fluids and electrolytes.
Quick Tip: Including hydrating foods alongside water intake supports optimal tissue repair.
Building a Healing Plate
Recovery requires more than a single “superfood.” It’s about creating a balanced plate with antioxidant-rich phytonutrients, collagen -activating nutrients, probiotics, anti-inflammatory spices, zinc and iron synergy, and hydration strategies.
Together, these foods give your body the fuel it needs to rebuild stronger tissue, reduce complications, and support a faster recovery.
Take good care—and Happy Holidays! ❄️✨🎄

Living with diabetes means being extra vigilant about health, especially when it comes to wound care. Even minor cuts or blisters can progress into serious complications due to delayed healing, poor circulation, and increased infection risks.
This makes wound care a crucial part of diabetes management. Fortunately, modern solutions and advanced therapies are transforming the way patients and caregivers approach diabetic wound care.
1. Unique Challenges in Diabetic Wound Healing
Diabetic wounds differ from ordinary wounds in several ways:
- Reduced Sensation (Neuropathy): Many patients experience nerve damage that diminishes their ability to feel pain, making them less likely to notice small injuries.
- Impaired Circulation: Restricted blood flow slows the delivery of oxygen and nutrients essential for healing.
- Higher Infection Risk: Elevated glucose levels provide a favorable environment for bacteria, increasing the chance of infections.
Together, these challenges often lead to delayed healing and chronic wounds, particularly on the feet, making proactive care essential.
2. Innovative Wound Care Management Therapies
Recent advancements in wound care are improving recovery outcomes for diabetic patients:
- Velvert® Dressings: Designed to create a protective, moist healing environment that accelerates tissue repair.
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): Uses gentle suction to remove fluids, reduce swelling, and promote faster healing.
- Hydrogel & Advanced Dressings: Maintain moisture balance, reduce pain, and minimize scarring.
- Antimicrobial Solutions: Dressings infused with silver or other agents help fight infection while supporting recovery.
These modern therapies go beyond basic bandaging, offering targeted solutions that actively support healing.
3. Importance of Early Detection and Timely Intervention
For diabetic patients, time is critical in wound management:
- Regular Self-Checks: Inspecting feet and legs daily for cuts, blisters, or redness.
- Professional Screenings: Routine check-ups with a podiatrist or healthcare provider.
- Prompt Action: Treating even minor wounds immediately with proper cleaning and dressings.
Catching a wound early can prevent it from progressing into a serious ulcer or infection that might require advanced medical intervention.
4. Integrating Preventive Care into Daily Life
Prevention is the cornerstone of diabetic wound care. Patients can reduce risks by adopting these practices:
- Daily Foot Inspections: Use a mirror or ask for assistance if needed.
- Skin Hydration: Keep skin moisturized to prevent cracks that can invite infections.
- Balanced Nutrition: A diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals supports healing.
- Protective Footwear: Always wear well-fitted shoes and socks to avoid friction and injury.
Incorporating these habits into daily routines ensures long-term protection.
5. Advanced Off-Loading Solutions
Pressure management plays a vital role in diabetic wound care:
- Total Contact Casting (TCC): Distributes weight evenly to reduce pressure on ulcers.
- Customized Diabetic Footwear: Specially designed shoes help minimize friction and pressure points.
- Pressure-Redistribution Insoles: Offer cushioning and support for patients with high-risk areas.
These solutions are critical for patients with foot ulcers, as they significantly reduce the chances of wound recurrence.
Empowering Diabetic Patients for Better Outcomes
Effective wound care is not just about healing—it’s about prevention, protection, and empowerment. By combining early detection, preventive strategies, advanced therapies, and innovative off-loading solutions, diabetic patients can significantly lower their risk of complications. With proactive care and modern tools, living with diabetes no longer has to mean living with chronic wounds.

Understanding Arthritis: How Compression Sleeves and Joint Supports Provide Relief
Arthritis is one of the most common chronic conditions affecting joints, with millions worldwide experiencing its impact daily. Characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, arthritis can significantly reduce mobility and quality of life.
While medical treatments and therapies are essential, patients often seek supportive solutions that offer daily relief and improve comfort.
Challenges Faced by Arthritis Patients
Living with arthritis is more than dealing with occasional discomfort—it involves:
- Persistent joint pain and stiffness, limiting day-to-day movement.
- Swelling and inflammation, which can worsen with activity.
- Reduced grip and mobility, affecting simple tasks like walking, lifting, or writing.
- Emotional impact, as long-term discomfort can lead to frustration, anxiety, and reduced independence.
These challenges highlight the importance of accessible, non-invasive support solutions.
How Orthopedic Support Products Help
Orthopedic aids like compression sleeves, joint supports, and braces are designed to complement medical management of arthritis. They provide:
- Gentle compression, improving circulation and reducing swelling resulting in a quicker recovery.
- Targeted support, stabilizing affected joints and limiting excessive strain.
- Improved comfort, easing pressure during movement or rest.
By addressing both pain and mobility limitations, these products serve as practical companions in daily arthritis care.
Benefits of Using Orthopedic Supports for Arthritis
Patients using compression sleeves and joint supports may experience:
- Pain reduction through controlled pressure and warmth.
- Decreased inflammation by enhancing blood flow and minimizing fluid buildup and an enhanced lymphatic drainage to flush out toxins.
- Better joint alignment and stabilisation reducing the risk of further strain or injury allowing the muscles and joints to function effectively.
- Enhanced confidence and mobility, allowing greater participation in daily activities.
Choosing the Right Product
Selecting the appropriate orthopedic support is essential for effectiveness:
- Compression sleeves: Best for continuous wear, mild-to-moderate pain, and swelling reduction.
- Knee or elbow supports: Ideal for stabilizing specific joints during activity and to redistribute your weight thereby reducing knee pain.
- Braces with adjustable straps: Suitable for patients requiring targeted support or customized pressure.
- Medical consultation: Always recommended to ensure the chosen product meets the patient’s condition and needs.
To maximize benefits, orthopedic supports should be incorporated into everyday routines:
- Wear during physical activity or prolonged standing to prevent flare-ups.
- Combine with gentle exercises recommended by physiotherapists.
- Use alongside healthy lifestyle practices, including weight management, balanced nutrition, and anti-inflammatory habits.
- Regularly monitor product fit and condition to maintain comfort and effectiveness.
Arthritis may be a lifelong condition, but it does not have to define a patient’s independence or comfort. Orthopedic products like compression sleeves and joint supports provide accessible, non-invasive relief—helping reduce pain, control inflammation, and support mobility.
By choosing the right product and integrating it into daily life, patients can regain confidence, ease, and a better quality of life.
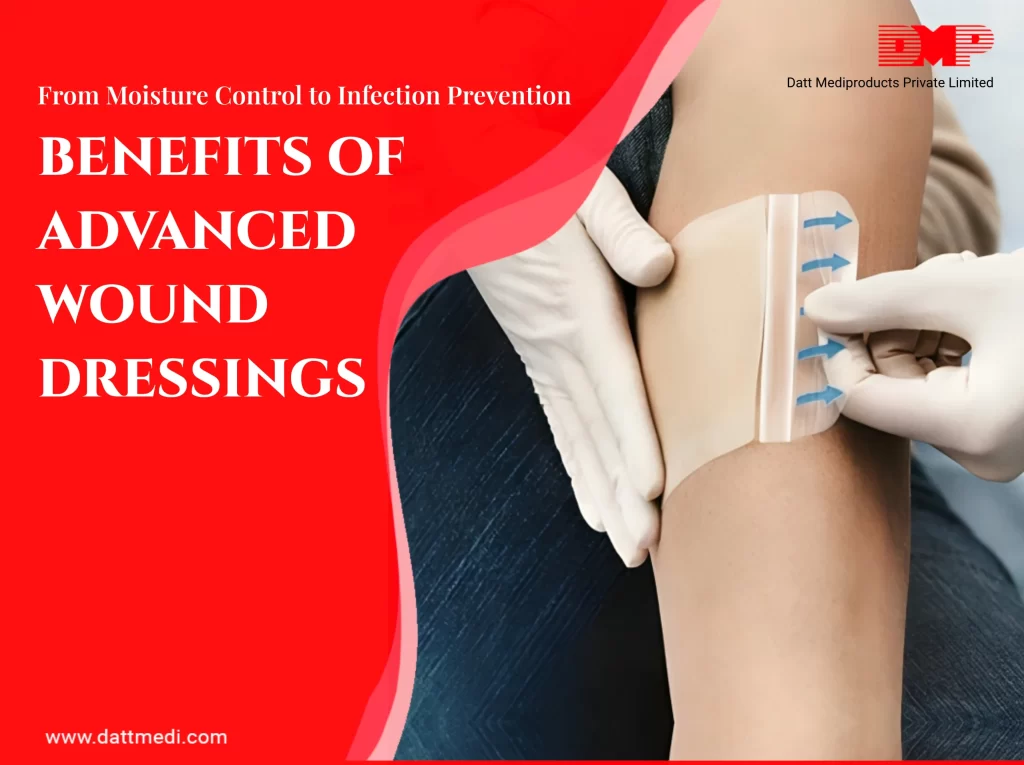
The Role of Advanced Wound Dressings in Accelerating Recovery for Complex Wounds
Traditional wound dressings were once viewed as simple barriers to shield an injury from external contaminants. Today, advanced wound dressings are revolutionizing wound care. They are active healing tools—designed not only to protect but also to accelerate recovery, reduce complications, and enhance patient comfort.
By responding to the needs of each wound, they support faster, more effective healing compared to conventional methods.
Beyond Basic Dressings: Creating a Bioactive Healing Environment
Unlike basic gauze pads, some advanced dressings provide a controlled, bioactive environment that stimulates wound repair. By incorporating various bioactive molecules such as antimicrobials. They:
- Maintain optimal moisture balance.
- Promote the healing process
- Regulate oxygen exchange.
- Some dressings offer antimicrobial protection when needed.
This environment allows cells to regenerate more efficiently, reduces infection risk, and shortens healing time.
Why Advanced Wound Dressings Are Essential for Complex & Chronic Wounds
Complex wounds such as diabetic ulcers, burns, and pressure sores often fail to heal with standard dressings. Advanced wound care solutions are essential because they:
- Restart stalled healing by balancing moisture and oxygen.
- Manage high exudate levels through superior absorption.
- Lower infection risks with antimicrobial properties.
These features make them indispensable for patients facing prolonged recovery.
Key Benefits of Advanced Wound Dressings
Using advanced dressings offers multiple clinical and patient-centered advantages:
- Moisture regulation – prevents drying and maceration.
- Reduced pain – cushioning and non-stick materials minimize discomfort during changes.
- Better comfort – lightweight, breathable materials allow mobility.
- Faster wound closure – optimized healing conditions accelerate recovery.
When to Choose Advanced Wound Dressings
Healthcare professionals should consider advanced dressings when:
- Healing has been delayed or stalled.
- The wound produces excessive drainage or exudate.
- There is a high risk of infection.
- Surgical incisions require enhanced healing protection.
In these cases, basic dressings often fail or take too long to heal the wound, while advanced dressings deliver targeted support.
Wounds That Benefit Most from Advanced Dressings
Certain conditions see the greatest benefit from these solutions:
- Diabetic ulcers – require moisture retention and infection control.
- Pressure sores (bedsores) – need pressure relief and high absorption.
- Surgical wounds – advanced dressings reduce infection risk and improve scarring.
- Burn injuries – delicate tissue heals faster with protective, moist dressings.
How to Choose the Right Advanced Wound Dressing
Selecting the correct dressing depends on the wound’s characteristics:
- Moist wounds → use absorbent foam or alginate dressings.
- Dry wounds → apply hydrogel dressings for hydration.
- Infected wounds → use antimicrobial dressings.
- Deep wounds → choose layered or cavity-fill dressings such as negative pressure therapy.
Matching dressing type to wound condition ensures maximum healing efficiency.
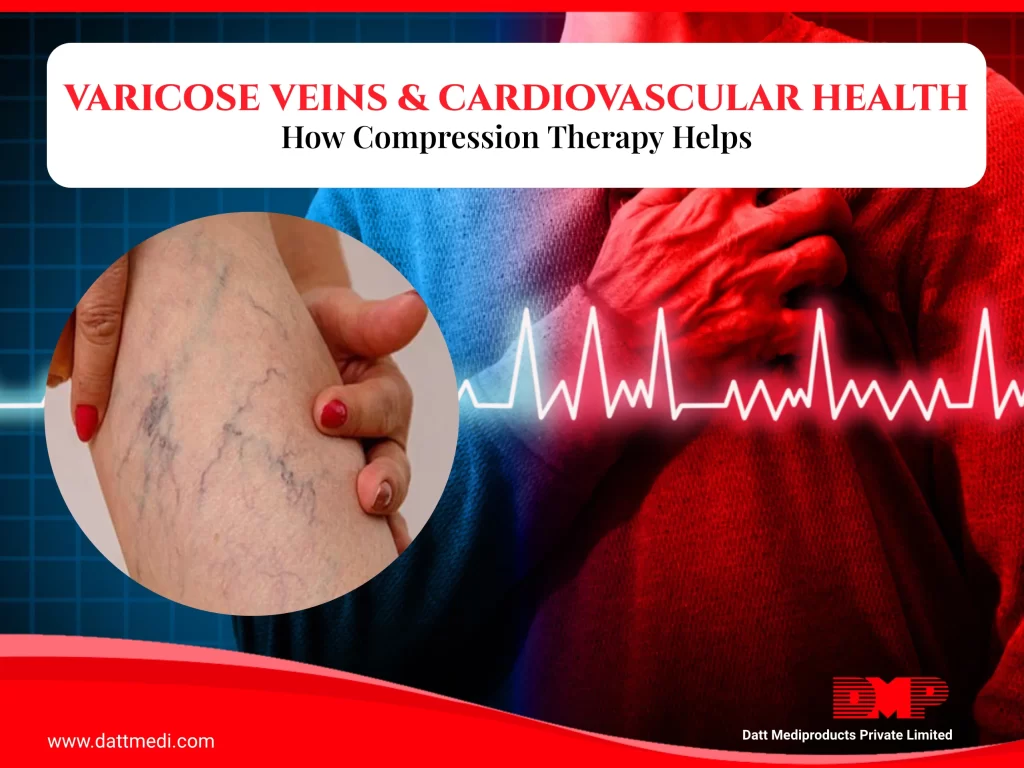
Understanding Venous Insufficiency: The Role of Compression in Managing Symptoms
World Heart Day, observed annually on September 29, focuses on promoting cardiovascular health worldwide. An essential but often overlooked aspect of cardiovascular wellness is venous health, which plays a critical role in overall circulation and mobility.
Compression therapy has emerged as a cornerstone in managing venous insufficiency and related disorders, offering effective support for improved circulation and symptom relief.
Understanding Venous Insufficiency and Varicose Veins
1. Venous Insufficiency:
This condition arises when the veins, especially in the lower limbs, fail to efficiently return blood to the heart. It results in blood pooling, leading to symptoms such as leg swelling, heaviness, pain, and fatigue. Normally one-way valves or muscles pump blood back to the hear, but in venous insufficiency the valves are weakened or damaged causing blood to flow backwards or pool in the legs.
2. Varicose Veins:
This is one of the by products of venous insufficiency. Caused by weakened vein walls and malfunctioning valves, varicose veins are dilated, twisted veins visible under the skin surface. These can cause discomfort, skin changes, and increase the risk of ulcers if left unmanaged.
Role of Compression Therapy in Venous Health
Compression therapy applies controlled, graduated pressure to the legs, enhancing venous return by supporting vein walls and valves. This mechanical assistance:
- Improves blood flow velocity
- Reduces venous pressure and pooling
- Minimizes edema (swelling) and associated discomfort and pain
- Improves microcirculation in tiny blood vessels which is crucial for tissue oxygenation and healing
Benefits of Compression Therapy for Cardiovascular Health
- Enhanced Circulation: Promotes efficient blood return to the heart, thereby reducing risks of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and venous stasis.
- Symptom Management: Compression alleviates pain, swelling, and skin changes, improving patient mobility and quality of life.
- Post-Surgical Recovery: Compression therapy accelerates healing after vein surgery or injury by controlling inflammation and supporting tissue repair.
Scientific Backing and Clinical Guidelines
Multiple clinical studies and guidelines from vascular health authorities endorse the use of compression therapy as a first-line, evidence-based treatment for venous insufficiency and related conditions.
Compression products that deliver consistent and graduated pressure are shown to significantly reduce recurrence rates of venous ulcers and improve functional outcomes.
How DMP Supports Your Venous Care Needs
At DMP, we provide a comprehensive portfolio of premium compression therapy products tailored to address diverse clinical requirements and patient needs. Our offerings are designed to support effective venous health management with a focus on comfort, durability, and therapeutic efficacy.
Velcare® Varicose Vein Stocking:
Engineered for superior comfort and long-lasting durability, these stockings are available in multiple compression classes to suit varying degrees of venous insufficiency and post-operative care. Velcare® is ideal for daily use, providing reliable support to alleviate symptoms associated with chronic venous conditions.
Velkomp® Compression Bandage:
Designed to deliver firm, adjustable compression, Velkomp® is recommended for managing post-injury recovery and chronic venous disorders. These inelastic, non-stretch bandages offer higher compression levels essential for controlling edema and supporting healing in cases of venous ulcers and lymphedema.
All our products are manufactured under strict quality controls and comply with international standards, including ISO 13485 and CE certification, ensuring consistent safety, reliability, and clinical effectiveness.
Venous health plays a pivotal role in overall cardiovascular wellness, making effective management essential to prevent complications and enhance quality of life.
Incorporating compression therapy into patient care protocols is a proven strategy that delivers measurable benefits, from symptom relief to accelerated recovery.
On this World Heart Day, we reaffirm our commitment to supporting healthcare professionals and patients with advanced compression solutions that align with the highest standards of care.
Early intervention and sustained management with DMP’s trusted products can significantly improve venous circulation and long-term cardiovascular health outcomes.

